
< Back
Bunsen burner
Definition
A Bunsen burner is a laboratory apparatus that produces a hot flame by mixing air with a small stream of gas.
The Bunsen burner is named after Robert Bunsen, a German chemist who invented it in 1855. It is a simple device that consists of a metal tube with a gas jet at the bottom. The gas jet is controlled by a valve, and the flame is produced by mixing the gas with air.
The Bunsen burner is used in laboratories to heat substances and to create flames of different sizes and temperatures. It is a versatile tool that is used in a variety of experiments.
The size and temperature of the flame produced by a Bunsen burner can be controlled by adjusting the gas flow and the air flow. A small flame with a low temperature is used for heating delicate substances, while a large flame with a high temperature is used for burning substances.
The Bunsen burner is a safe piece of equipment when used properly. However, there are some safety precautions that should be taken when using a Bunsen burner. These precautions include:
- Always wear safety goggles when using a Bunsen burner.
- Never leave a Bunsen burner unattended.
- Turn off the gas when you are finished using the burner.
- Do not point the flame at yourself or other people.
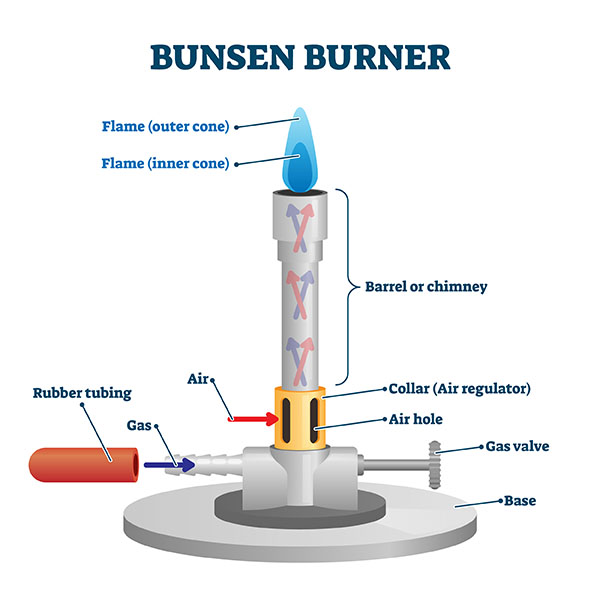
Here are some of the parts of a Bunsen burner:
- Base: The base is the bottom part of the Bunsen burner. It is made of metal and it provides a stable base for the burner.
- Base of Bunsen burner
- Gas inlet: The gas inlet is the opening at the bottom of the base that the gas enters the burner.
- Gas inlet of Bunsen burner
- Tubing: The tubing is the metal tube that carries the gas from the gas inlet to the gas jet.
- Tubing of Bunsen burner
- Gas jet: The gas jet is the opening at the top of the tubing that the gas exits the burner.
- Gas jet of Bunsen burner
- Air holes: The air holes are the small holes in the base of the burner that allow air to mix with the gas.
- Air holes of Bunsen burner
- Valve: The valve is the knob on the side of the burner that controls the flow of gas.
- Valve of Bunsen burner
- The Bunsen burner is a versatile and useful piece of laboratory equipment. It is a safe piece of equipment when used properly, but it is important to follow safety precautions when using it.
How can the word be used?
The Bunsen burner was used to heat the test tube.
Different forms of the word
Noun: Bunsen burner.
Plural: Bunsen burners.
Etymology
The word "Bunsen burner" is named after its inventor, Robert Wilhelm Bunsen, a German chemist who lived from 1811 to 1899. Bunsen developed the burner in the 1850s as a more efficient and controllable way to heat chemicals in the laboratory.
Question
What are the main parts of the Bunsen burner?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
What are the different types of flames produced by a Bunsen burner?
Answer:
There are three main types of flames produced by a Bunsen burner:
The soft flame is a low-temperature flame that is used for heating delicate substances. It is produced by closing the air holes so that there is little air mixing with the gas. The flame is yellow and has a small, pointed tip.
Soft flame of Bunsen burner.
The medium flame is a medium-temperature flame that is used for most laboratory work. It is produced by opening the air holes slightly so that there is some air mixing with the gas. The flame is blue and has a slightly larger, rounded tip.
Medium flame of Bunsen burner.
The hot flame is a high-temperature flame that is used for burning substances. It is produced by opening the air holes fully so that there is a lot of air mixing with the gas. The flame is blue and has a large, bushy tip.
Hot flame of Bunsen burner.
The type of flame produced by a Bunsen burner can be controlled by adjusting the gas flow and the air flow. A small flame with a low temperature is used for heating delicate substances, while a large flame with a high temperature is used for burning substances.