
< Back
species
Definition
A species is a group of organisms that are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. This means that they share a common gene pool and can pass on their genes to their offspring.
Species are important because they help to maintain biodiversity. Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, and it is important for the health of the planet. Each species plays a role in the ecosystem, and if a species goes extinct, it can have a negative impact on the other species in the ecosystem.
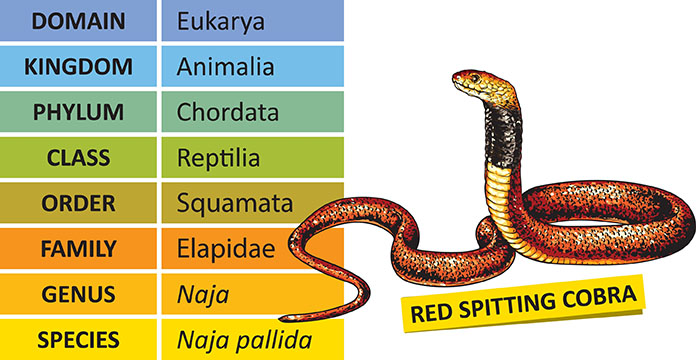
There are many different ways to classify species. One common way is to use the Linnaean system, which was developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. The Linnaean system uses a hierarchical system of classification to group organisms into different categories, such as genus, family, order, class, phylum, and kingdom.
How can the word be used?
The Amazon rainforest is home to many different species of plants and animals.
Different forms of the word
Noun: species (plural: species).
Adjective: specific.
Adverb: specifically.
Verb: to speciate.
Etymology
The word "species" comes from the Latin word "species", which means "appearance" or "kind". It was first used in English in the 16th century to refer to a group of organisms that are similar in appearance and can interbreed.
The word "specific" comes from the same Latin root as "species". It means "of or relating to a particular species".
The word "specifically" means "in a specific way" or "precisely".
The word "to speciate" means "to form a new species".
Question
What is a species?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Define the term "species" and explain the importance of species classification in biology, emphasising its role in understanding biodiversity and evolution.
Answer:
A species is a fundamental biological concept that refers to a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring under natural conditions. This classification reflects a shared gene pool and distinctive characteristics that distinguish one species from another.
Species classification is a cornerstone of biology as it provides a systematic framework for organising and categorising the immense diversity of life on Earth. By assigning organisms to specific species, scientists can study their unique traits, behaviours, and interactions within ecosystems.
Furthermore, species classification plays a pivotal role in understanding the process of evolution. The concept of a species serves as the fundamental unit upon which natural selection acts. Over time, variations within and between species accumulate, contributing to the formation of new species. By studying the evolutionary history and relationships among species, scientists gain insights into the origin and diversification of life forms.
Biodiversity, the variety of life forms, is essential for ecosystem stability and resilience. Proper species classification allows scientists to assess the health of ecosystems, monitor changes, and implement conservation strategies to protect endangered species.