
< Back
solvent
Definition
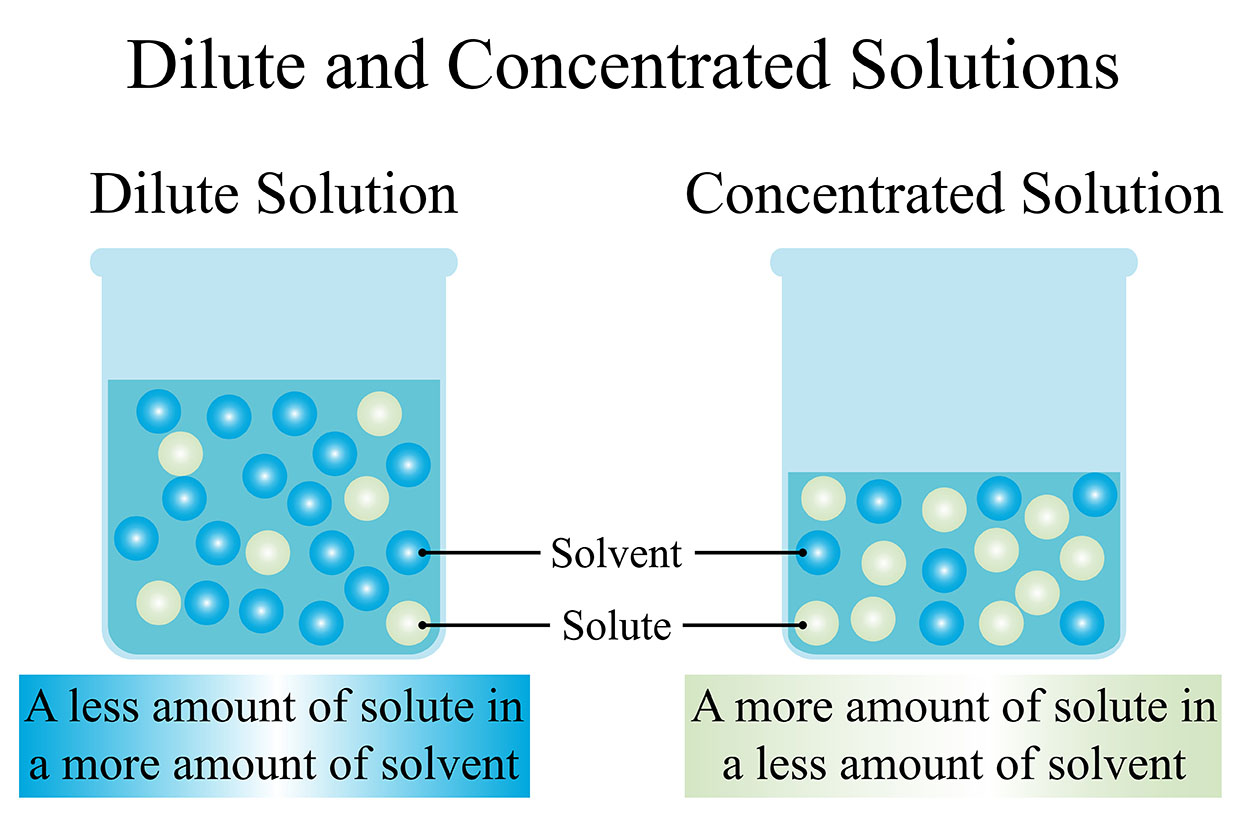
In chemistry, a solvent is a substance that can dissolve other substances. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The solvent is the liquid that dissolves the solute. The solute is the substance that is dissolved in the solvent.
The solvent is the major component of a solution. The solute is the minor component of a solution.
The solvent and solute must be miscible, which means that they can mix together to form a solution. Not all substances are miscible. For example, oil and water are immiscible, which means that they cannot mix together to form a solution.
The solubility of a solute is the amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature. The solubility of a solute depends on the chemical properties of the solute and solvent.
For example, sugar is soluble in water. This means that sugar can be dissolved in water to form a solution.
Salt is also soluble in water. Salt is soluble in water because the salt molecules can dissociate into ions. The sodium ions are positive, and the chloride ions are negative. The water molecules can surround the ions, and this helps to dissolve the salt.
The solubility of a solute can be affected by temperature. In general, the solubility of a solute increases with temperature. This is because the molecules of the solute have more energy at higher temperatures, and they are more likely to interact with the solvent molecules.
How can the word be used?
The solvent was heated to increase its dissolving power.
Different forms of the word
Solvent (adjective): A substance that can dissolve another substance. For example, water is a solvent for salt.
Solvent (noun): A liquid that can dissolve other substances. For example, paint thinner is a solvent for paint.
Solvent (verb): To dissolve a substance in a solvent. For example, to dissolve salt in water, you would add salt to water and stir until the salt is dissolved.
Etymology
The etymology of the word "solvent" can be traced back to the Latin word "solventem", which is the present participle of the verb "solvere", meaning "to loosen" or "to dissolve". The word "solvent" first appeared in English in the 1650s, and it has been used to refer to a substance that can dissolve another substance ever since.
Question
What is a solvent?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Define the term "solvent" and explain its role in creating solutions, illustrating with real-world examples.
Answer:
A solvent is a substance, usually a liquid, capable of dissolving other substances to form a solution. It is a crucial component in the creation of solutions, facilitating the dispersion and even distribution of solute particles within the mixture.
Real-world examples highlight the role of solvents. When sugar is dissolved in water to make a sweetened beverage, water acts as the solvent and sugar is the solute. In this case, water molecules surround and disperse the sugar particles, allowing for a uniform mixture. Similarly, in household cleaning solutions, the solvent, often water or a water-based solution, disperses the solute (cleaning agents) to effectively clean surfaces.
The interaction between solute and solvent involves breaking the intermolecular forces in the solute, allowing the solvent molecules to surround and solvate the solute particles. This process leads to a well-mixed and homogeneous solution.
Solvents have applications in various fields, from chemistry laboratories to industrial processes. They enable the creation of solutions with distinct properties, making them essential for tasks ranging from pharmaceutical formulations to ink production. Understanding the role of solvents provides insight into the science of solutions and their wide-ranging utility in our daily lives.