
< Back
evolution
Definition
Evolution is the change in the genetic makeup of a population over time. This change is caused by natural selection, which is the process by which organisms that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Natural selection is based on the idea that there is variation in the genetic makeup of a population. This variation is caused by mutations, which are changes in the DNA of an organism. Some mutations are beneficial, meaning that they give the organism an advantage in its environment. Other mutations are harmful, meaning that they give the organism a disadvantage in its environment.
Organisms that have beneficial mutations are more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that the beneficial mutations will become more common in the population over time. Over many generations, this process of natural selection can lead to the evolution of new species.
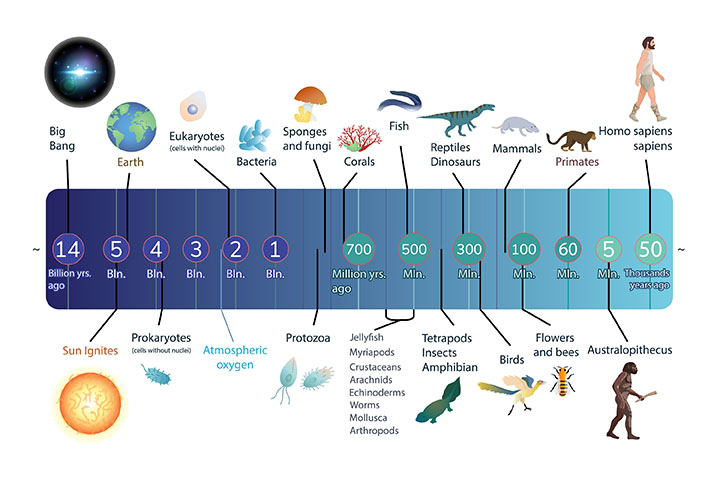
Evolution is a very important process. It is the reason why we exist today. It is also the reason why there is so much diversity in life on Earth.
How can the word be used?
The theory of evolution is the scientific explanation for how evolution occurs.
Different forms of the word
Noun: evolution, evolutionary process, development.
Adjective: evolutionary, evolving.
Verb: to evolve, to develop.
Synonyms: change, progress, transformation.
Etymology
The word "evolution" comes from the Latin word evolvere, which means "to unroll" or "to unfold." It was first used in English in the 17th century, and it is still used today to refer to the process by which living things change over time.
Question
What is evolution?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the concept of evolution and the mechanisms that drive it. Describe natural selection as proposed by Charles Darwin and its role in the adaptation of species over time. Provide examples of how evolution has led to the diversity of life on Earth, such as the development of different species and the emergence of new traits. Discuss the significance of studying evolution in understanding the history of life and its applications in fields like medicine and agriculture.
Answer:
Evolution is the process of gradual change in the inherited traits of a population over successive generations. It occurs through natural selection, as proposed by Charles Darwin. Natural selection is driven by variations in traits that confer advantages or disadvantages in a particular environment. Organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass on their traits to the next generation, leading to the adaptation of species to their surroundings.
Examples of evolution include the development of various species from common ancestors and the emergence of new traits, such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Evolution has led to the incredible diversity of life on Earth, from the myriad of species to the complex behaviours and adaptations observed in organisms.
Studying evolution is essential in understanding the history of life on Earth and the processes that have shaped the natural world. It has practical applications in fields like medicine, where understanding evolutionary processes helps combat diseases and develop new treatments. In agriculture, knowledge of evolution aids in breeding programs to improve crop resistance and productivity. A comprehensive understanding of evolution contributes to our appreciation of the interconnectedness of all living organisms and the complexity of the natural world.