
< Back
brain
Definition
The brain is the control centre of the body. It is responsible for everything from thinking and feeling to moving and sensing. The brain is made up of billions of neurons, which are cells that transmit electrical signals. These signals allow the brain to communicate with the rest of the body and to control its functions.
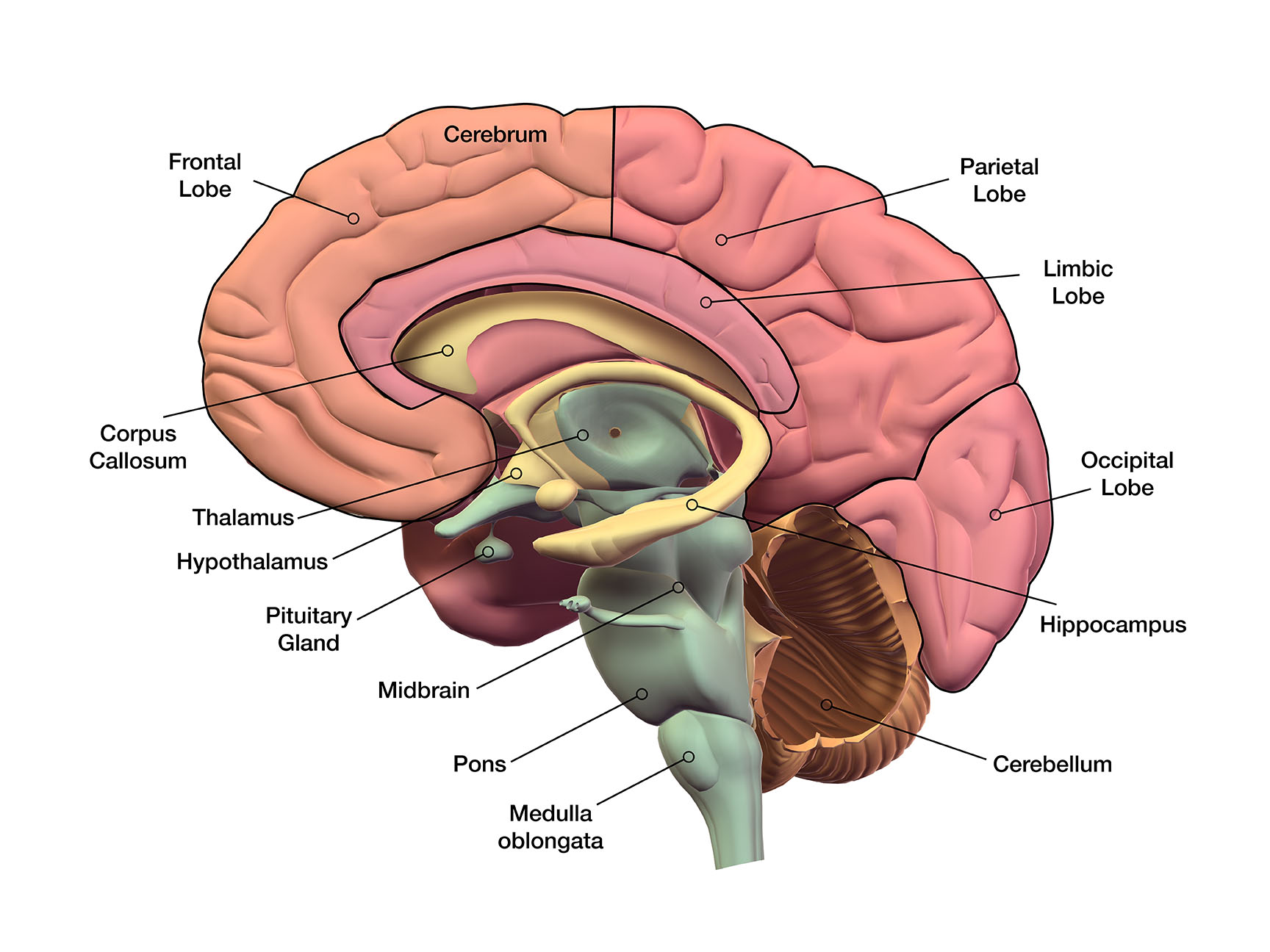
The brain is a complex organ, and it is still not fully understood. However, scientists have learned a lot about how the brain works. They know that the brain is divided into different regions, each of which is responsible for different functions. For example, the frontal lobe is responsible for thinking and planning, while the temporal lobe is responsible for hearing and memory.
The brain is also constantly changing. As we learn and experience new things, the brain's connections are strengthened. This is why it is important to challenge our brains and to learn new things throughout our lives.
How can the word be used?
The brain is the most important organ in the body.
Different forms of the word
Noun:
brain (the organ that controls thought, feeling, and movement).
brains (intelligence or cleverness).
brainiac (a very intelligent person).
Adjective:
brainy (intelligent or clever).
Verb:
to brain (to injure or damage the brain).
Etymology
The word "brain" comes from the Old English word "brēgen," which means "the organ that controls thought and feeling." The Old English word "brēgen" is related to the Old Norse word "braginn" and the German word "Brein.".
Question
What do the neurons in your brain do?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Define the term "brain" and explain its importance in the human body. Describe the primary functions of the brain and its role in coordinating various bodily activities.
Answer:
The brain is a complex organ that serves as the command centre of the central nervous system in the human body. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating various bodily activities and processes.
Functions of the Brain:
Cognition and Thinking: The brain is the centre of cognitive functions, including perception, memory, reasoning, and problem-solving.
Motor Control: It controls voluntary and involuntary movements, enabling the execution of daily activities and reflexes.
Sensory Processing: The brain receives and processes sensory information from the body's senses (sight, hearing, touch, taste, smell) and interprets the external environment.
Homeostasis: The brain regulates internal body functions to maintain a stable environment, such as body temperature, blood pressure, and hormone levels.
Emotions and Behavior: It plays a significant role in emotions, mood regulation, and behavioural responses to different stimuli.
Language and Communication: The brain facilitates language comprehension, speech production, and communication skills.
Autonomic Functions: The brain controls involuntary functions, such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
The brain's importance in the human body lies in its ability to integrate information from various sources and respond appropriately to stimuli, ensuring the body's proper functioning and survival. Its complex structure and interconnectedness with other body systems make it one of the most critical organs for human health and functioning.