

Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a wave. It is measured in meters. Wavelength is related to the frequency of the wave by the equation:
wavelength = speed of wave / frequency
Where:
The wavelength of a wave determines how much energy it carries. The shorter the wavelength, the more energy the wave carries.
Wavelength is an important property of waves and it is used in many different applications, such as sonar, radar, and spectroscopy.
The wavelength of light is the distance between two successive peaks of the light wave.
Noun: the distance between two successive peaks of a wave.
The word "wavelength" comes from the combination of the words "wave" and "length".
The word "wave" comes from the Old English word "wāgan", which means "to move to and fro".
The word "length" comes from the Old English word "lengthe", which means "the extent of something from end to end".
The first recorded use of the word "wavelength" was in the 19th century.
What happens when a wave length chances?
Question:
Explain the concept of wavelength in relation to waves. Discuss how wavelength influences the properties of waves and give examples of how different wavelengths are encountered in everyday life.
Answer:
Wavelength is a fundamental characteristic of waves that refers to the distance between two consecutive points on a wave that are in phase, such as two crests or two troughs. It plays a significant role in determining various properties of waves and their behaviour.
In general, longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies, while shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies. This relationship is governed by the wave equation, where speed equals frequency multiplied by wavelength.
For example, in electromagnetic waves, different wavelengths of light manifest as different colours. Visible light contains a range of colours, each corresponding to a specific wavelength within the electromagnetic spectrum.
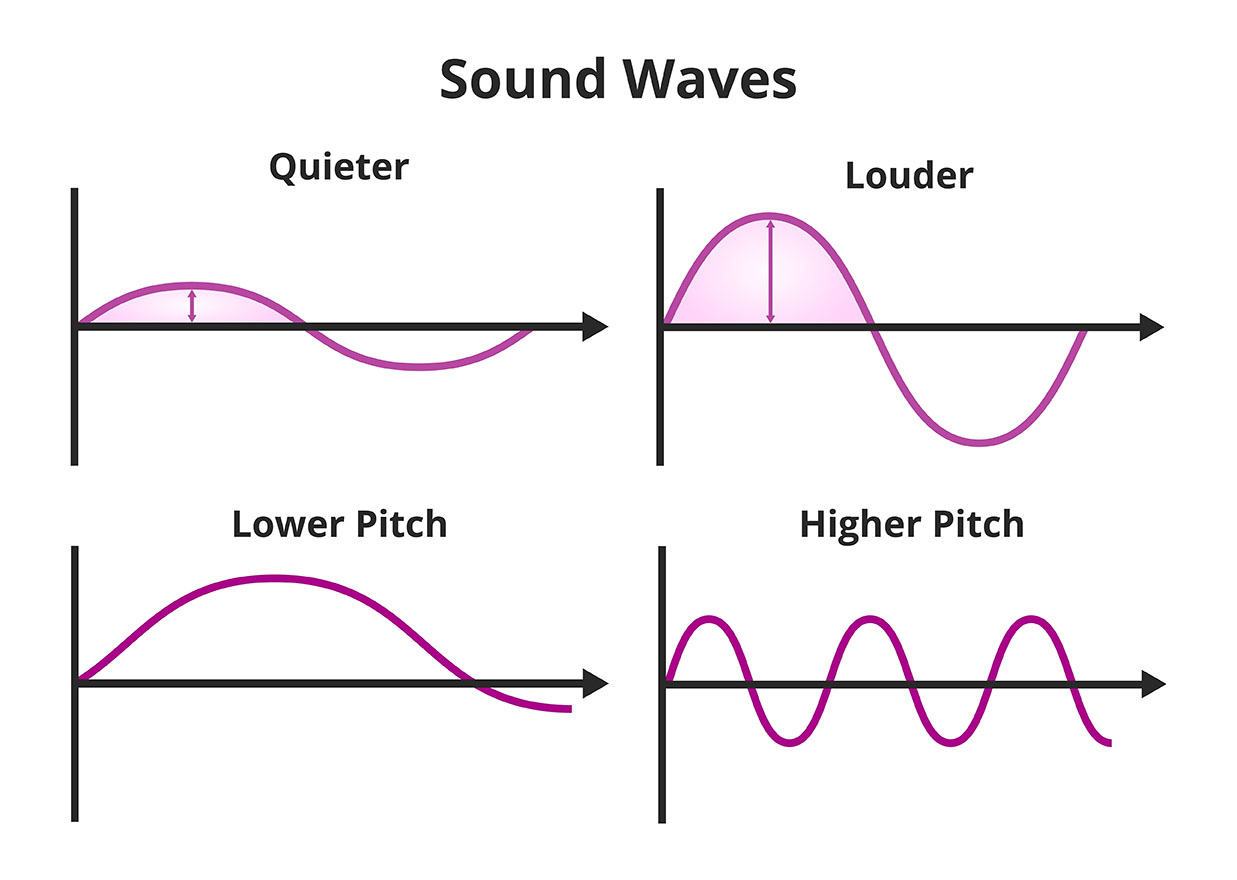
In sound waves, wavelength affects the pitch of the sound. Higher-pitched sounds have shorter wavelengths, while lower-pitched sounds have longer wavelengths.
Radio waves, used in wireless communication, have much longer wavelengths compared to visible light. This is why radio waves can travel through walls and other obstacles more effectively, allowing them to transmit information over long distances.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.