

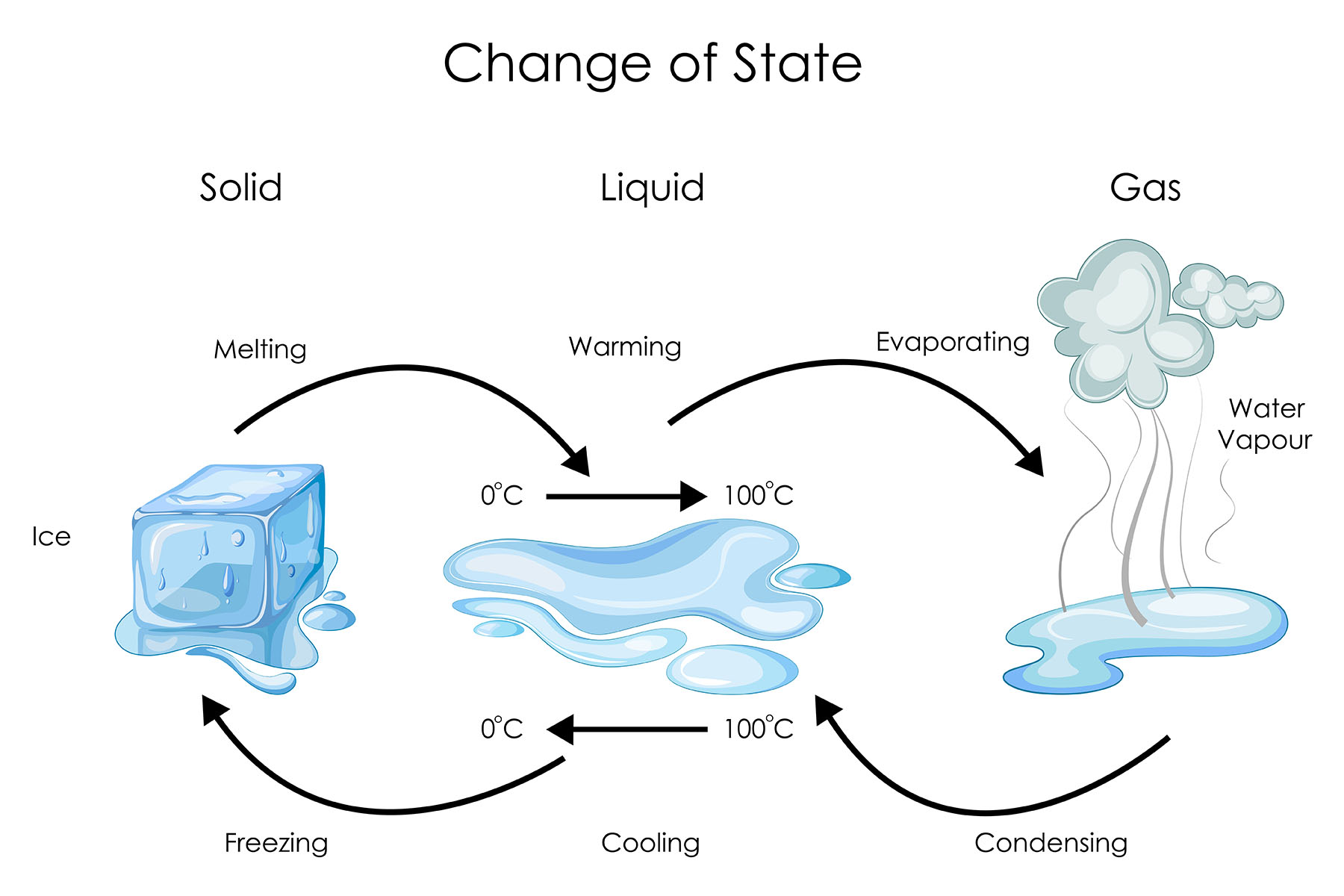
Water vapour is the gaseous state of water. It is formed when water molecules escape from the liquid state and enter the gas state. This can happen when water is heated, when it is exposed to a vacuum, or when it is mixed with another gas. Water vapour is invisible to the naked eye, but it can be detected by its effects, such as the formation of clouds and fog.
The water vapour in the air condenses to form clouds.
Noun: the gaseous state of water.
Adjective: relating to water vapour.
The word "water vapor" comes from the combination of the words "water" and "vapor".
The word "water" comes from the Old English word "wæter", which means "water".
The word "vapor" comes from the Latin word "vapor", which means "steam" or "mist".
The first recorded use of the word "water vapor" was in the 17th century.
Where might you find water vapour?
Question:
Explain the concept of water vapour and its role in the water cycle. Discuss how water vapour contributes to cloud formation, precipitation, and weather patterns.
Answer:
Water vapour is the gaseous form of water present in the Earth's atmosphere. It plays a crucial role in the water cycle, facilitating the continuous movement of water between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere.
As part of the water cycle, water vapour is generated through the process of evaporation, where liquid water is converted into water vapour due to solar energy. The water vapour then rises into the atmosphere, contributing to the overall humidity of the air.
Water vapour is a key factor in cloud formation. When warm, moist air rises, it cools and condenses around tiny particles, forming water droplets or ice crystals. These droplets cluster together to create clouds, which are essential for various meteorological phenomena, including precipitation.
Clouds release moisture in the form of precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail, depending on atmospheric conditions. Water vapour's role in cloud formation and precipitation is central to maintaining freshwater resources and supporting ecosystems.
Furthermore, water vapour influences weather patterns and atmospheric conditions. Changes in temperature and humidity levels impact the amount of water vapour the air can hold, influencing cloud cover, rainfall, and the development of weather systems.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.