
vertebrate
Definition
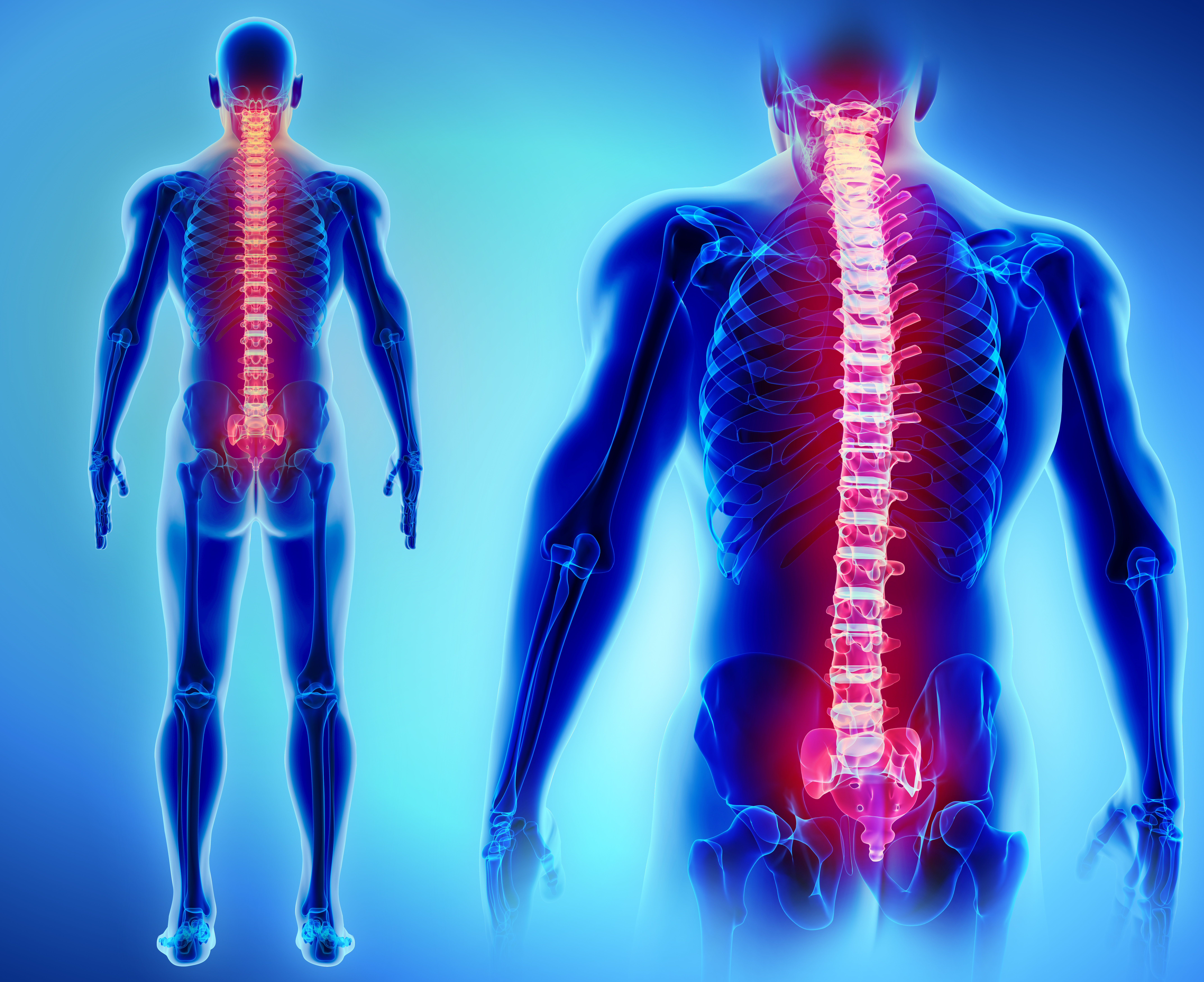
Vertebrate is a term used to describe animals that have a backbone. The backbone is a long, flexible structure that supports the body and protects the spinal cord.
Vertebrates are found in all parts of the world and come in all shapes and sizes. Some vertebrates, such as fish, live in water. Others, such as birds, live in the air. And still others, such as mammals, live on land.
Vertebrates are also classified into five different groups: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Each group has its own unique features:
Fish are the most diverse group of vertebrates. They come in all shapes and sizes, from tiny minnows to giant whales.
Amphibians are the first vertebrates to live on land. They can breathe air and water, and they lay their eggs in water.
Reptiles are the first vertebrates to have scales. They include snakes, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles.
Birds are the only vertebrates that can fly. They have feathers and wings, and they lay their eggs in nests.
Mammals are the most intelligent vertebrates. They have hair and mammary glands, and they give birth to live young.
How can the word be used?
The human spine is made up of 33 vertebrae.
Different forms of the word
Noun: an animal with a backbone.
Adjective: of or relating to vertebrates.
Etymology
The word "vertebrate" comes from the Latin word "vertebratus", which means "having a jointed backbone".
The first recorded use of the word "vertebrate" in English was in the 17th century.
Question
What are vertebrates?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Define a vertebrate and provide an example of an adaptation in vertebrates that has contributed to their success in different habitats.
Answer:
A vertebrate is an animal belonging to a diverse group characterized by the presence of a backbone or vertebral column. This structural feature provides support, and protection for the spinal cord, and serves as an anchor for muscles. Vertebrates include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
An example of an adaptation in vertebrates that has led to their success in different habitats is the evolution of feathers in birds. Feathers are lightweight, modified scales that provide insulation, enable flight, and aid in courtship displays. For instance, the streamlined shape of feathers facilitates efficient flight, enabling birds to migrate vast distances and exploit various ecological niches. In colder climates, feathers provide essential insulation, allowing birds to maintain their body temperature and conserve energy.
Moreover, feathers play a crucial role in courtship rituals and territorial displays, enhancing reproductive success. This adaptation has contributed to the remarkable diversity of bird species and their ability to inhabit diverse environments, from tropical rainforests to deserts and polar regions. The evolution of feathers showcases the remarkable adaptability of vertebrates, allowing them to thrive in various habitats by developing unique features that suit their specific needs.