
trimester
Definition
A trimester is a division of the academic year into three equal terms. It is a system of dividing the school year into three terms of approximately twelve weeks each.
The trimester system is used in some schools and colleges, especially in the United States. It is sometimes used in conjunction with a semester system, in which the academic year is divided into two terms of approximately sixteen weeks each.
The trimester system has several advantages over the semester system. It allows for more flexibility in scheduling, and it gives students more time to learn the material.
However, the trimester system also has some disadvantages. It can be more difficult for students to keep up with the workload, and it can be more difficult for professors to plan their courses.
How can the word be used?
The patient is in the third trimester of their cancer treatment, and they are hopeful that they will be able to complete the treatment successfully.
Different forms of the word
Noun:
a period of three months.
Etymology
The word "trimester" comes from the French word "trimestre", which means "three months".
The first recorded use of the word "trimester" in English was in the 17th century.
The word "trimester" is a French word, and it is related to the Latin word "trimestris", which also means "three months".
Question
How long is a trimester?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the concept of trimester in the context of human pregnancy. Describe the key developmental milestones and changes that occur during each trimester. Discuss the importance of medical care and monitoring throughout pregnancy.
Answer:
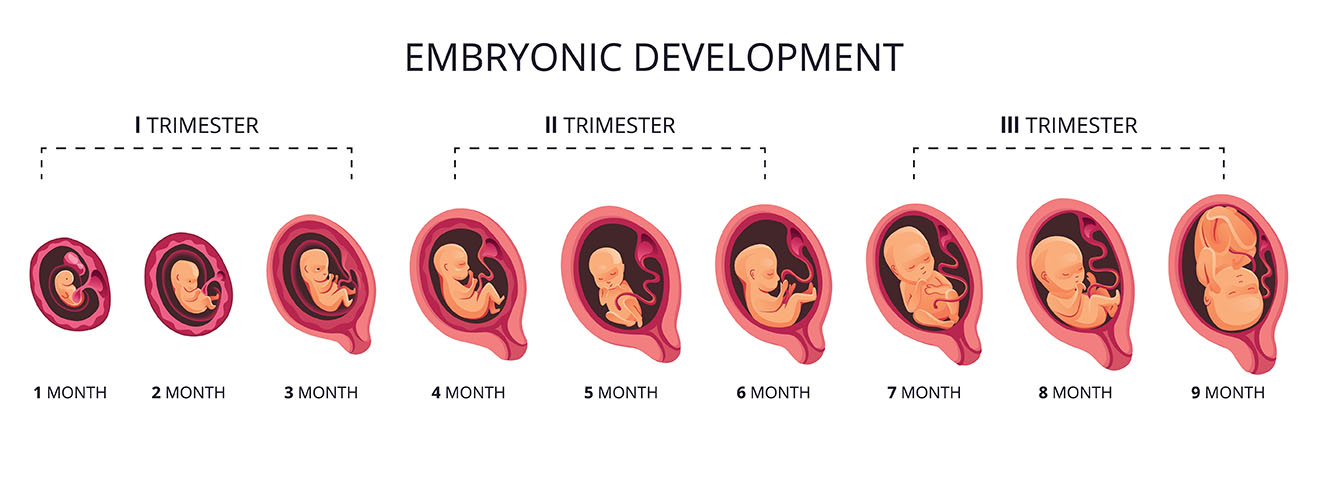
The concept of trimester refers to the division of a human pregnancy into three distinct phases, each lasting approximately three months. These trimesters provide a framework to understand the progression of foetal development and maternal changes during pregnancy.
During the first trimester (weeks 1-12), significant developmental milestones occur. The fertilised egg implants in the uterus, rapidly dividing and forming the embryo. Organs begin to take shape, and the heart starts beating. Early pregnancy symptoms such as morning sickness and fatigue may be experienced. The second trimester (weeks 13-28) sees further growth and refinement of organs. The baby's movements become more noticeable to the mother, and gender can be determined. By the third trimester (weeks 29-40), the foetus gains weight, its organs mature, and it prepares for birth. The mother may experience discomfort, increased size, and contractions as the due date approaches.
Medical care and monitoring are crucial throughout pregnancy. Regular prenatal check-ups allow healthcare professionals to assess the health of both the mother and the developing foetus. Monitoring factors such as blood pressure, weight gain, and foetal growth helps detect any potential issues early, ensuring timely intervention if needed. Proper nutrition, rest, and prenatal vitamins are essential for a healthy pregnancy.