
sublimation
Definition
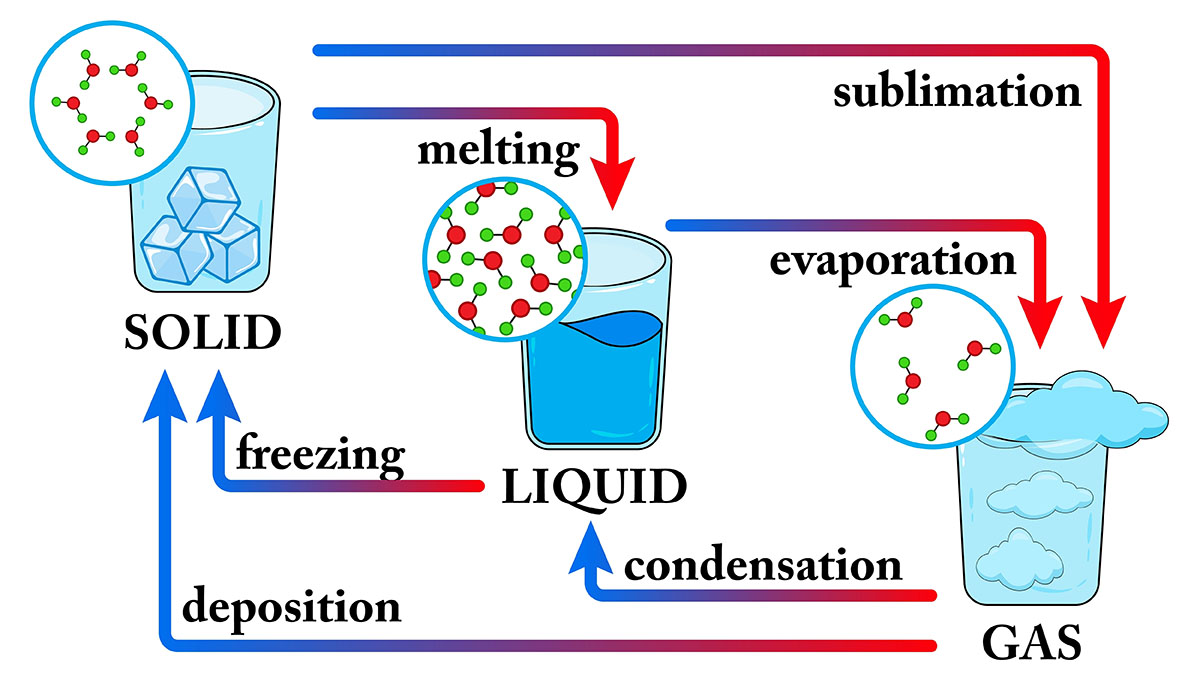
Sublimation is a phase transition in which a substance goes directly from the solid state to the gaseous state without passing through the liquid state. This happens when the substance's vapour pressure is greater than the atmospheric pressure.
The vapour pressure of a substance is the pressure exerted by its vapour in equilibrium with its solid or liquid phase. The vapour pressure of a substance increases as the temperature of the substance increases.
Sublimation is a reversible process. This means that the gas can condense back into the solid state. The condensation of a gas is called deposition.
Sublimation is a common process in nature. For example, snow and ice sublimate on high mountains, where the atmospheric pressure is low. This is why snow and ice can disappear even when the temperature is below freezing.
Sublimation is also used in many industrial processes. For example, dry ice is used to preserve food and to create fog effects in movies and theatre productions.
How can the word be used?
The artist sublimated his sexual energy into his work.
Different forms of the word
Noun: sublimation (plural: sublimations).
Verb: to sublimate.
Etymology
The word "sublimation" comes from the Latin word "sublimare", which means "to raise up" or "to elevate". It was first used in English in the 17th century.
The word "to sublimate" means to change from a solid to a gas without going through the liquid state. It can also mean to change from one form to another without passing through an intermediate form.
Question
What is sublimation?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the process of sublimation and provide examples of substances that undergo sublimation. Discuss the factors that influence sublimation rates and how this phenomenon is utilised in everyday applications.
Answer:
Sublimation is the phase transition in which a substance directly changes from a solid to a gaseous state without passing through the liquid phase. This occurs when the vapour pressure of the solid surpasses the atmospheric pressure. A familiar example of sublimation is dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) transforming into carbon dioxide gas without becoming a liquid.
Substances that commonly undergo sublimation include volatile compounds like camphor, naphthalene (found in mothballs), and certain volatile chemicals. Iodine crystals also sublime when heated.
Factors affecting sublimation rates include temperature, pressure, and the surface area of the solid. Higher temperatures and reduced pressure favour faster sublimation. This phenomenon finds practical use in freeze-drying, a process that removes moisture from food, pharmaceuticals, and other products without causing significant damage.