

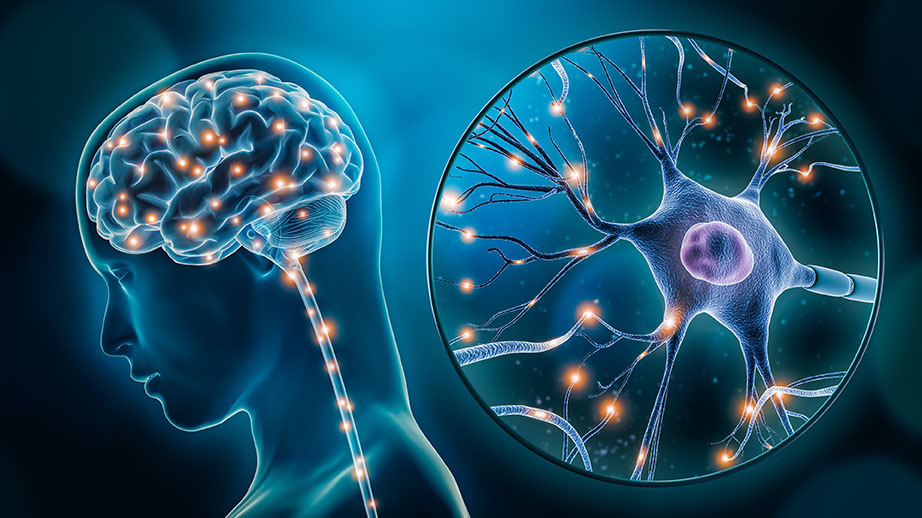
A stimulant is a drug that increases the activity of the central nervous system. This can lead to a number of effects, including increased alertness, wakefulness, and energy levels. Stimulants can also suppress appetite and increase heart rate and blood pressure. Some common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine.
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that send signals between nerve cells. Stimulants increase the levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are associated with alertness, wakefulness, and motivation.
Stimulants can have both positive and negative effects. They can be used to treat a variety of medical conditions, such as ADHD and narcolepsy. However, they can also be addictive and can have serious side effects, such as anxiety, insomnia, and heart problems.
It is important to use stimulants safely and responsibly. If you are considering using a stimulant, talk to your doctor first.
The drug was used as a stimulant.
Noun: stimulant (plural: stimulants).
Adjective: stimulating.
Verb: to stimulate.
The word "stimulant" comes from the Latin word "stimulare", which means "to prick" or "to goad". It was first used in English in the 17th century.
The word "stimulating" means "producing a stimulating effect".
The word "to stimulate" means "to excite or rouse to activity".
What is a stimulant?
Question:
Explain the effects of stimulants on the human nervous system and their potential benefits and drawbacks. Discuss a common stimulant, its mode of action, and its impact on cognitive function and alertness.
Answer:
Stimulants are substances that increase activity in the central nervous system, resulting in heightened alertness, energy, and cognitive function. One common stimulant is caffeine, found in beverages like coffee and tea. Caffeine functions by blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation.
Upon consumption, caffeine prevents adenosine from binding to its receptors, leading to increased neural activity. This results in heightened wakefulness and improved cognitive performance. However, excessive consumption or dependency on caffeine can lead to negative effects such as insomnia, restlessness, and elevated heart rate.
Caffeine's ability to enhance cognitive function and maintain alertness has made it a widely used and socially accepted stimulant. Many people rely on caffeine to combat fatigue and increase focus, especially during demanding tasks or long periods of work or study. It is important to strike a balance, as moderate caffeine consumption can offer benefits, while excessive intake may lead to undesirable outcomes. Understanding the effects of stimulants like caffeine on the nervous system enables individuals to make informed choices about their consumption and its potential impact on overall well-being.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.