

In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
The substances in a solution cannot be separated by physical means, such as filtering or sieving. This is because the particles in a solution are very small and they are evenly distributed throughout the solution.
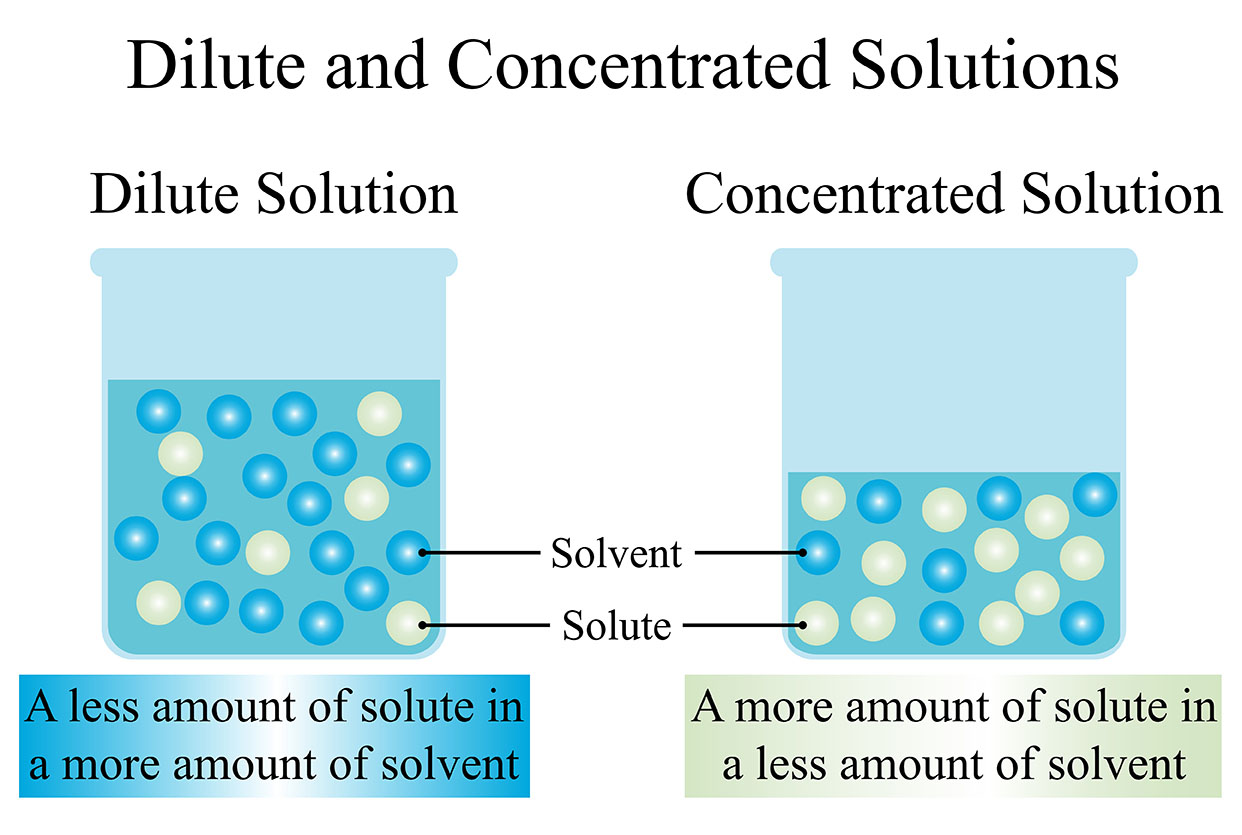
The solvent is the liquid that dissolves the solute. The solute is the substance that is dissolved in the solvent.
In the example of salt water, the solvent is water and the solute is salt. The salt molecules are evenly mixed with the water molecules.
The solubility of a solute is the amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature. The solubility of a solute depends on the chemical properties of the solute and solvent.
For example, sugar is soluble in water. This means that sugar can be dissolved in water to form a solution.
Salt is also soluble in water. Salt is soluble in water because the salt molecules can dissociate into ions. The sodium ions are positive, and the chloride ions are negative. The water molecules can surround the ions, and this helps to dissolve the salt.
The solubility of a solute can be affected by temperature. In general, the solubility of a solute increases with temperature. This is because the molecules of the solute have more energy at higher temperatures, and they are more likely to interact with the solvent molecules.
The orange concentrate and water made up the solution.
Noun:
Verb:
The word "solution" comes from the Latin word "solutio", which means "loosening" or "unfastening". This is related to the verb "solvere", which means "to loosen". The word "solution" can be used in a variety of contexts, but it most commonly refers to a mixture of two or more substances in which one substance is dissolved in another. For example, salt water is a solution of salt in water.
The etymology of the word "etymology" is also related to the word "solution". The word "etymology" comes from the Greek words "etymon" and "logos", which mean "true meaning" and "word" respectively. So, etymology is the study of the true meaning of words, and it can be used to trace the history of a word back to its origins.
In the case of the word "solution", the etymology can be traced back to the Latin word "solutio". This word was borrowed into Old French, and then into Middle English. The Middle English word "solucion" eventually developed into the modern English word "solution".
What is a solution?
Question:
Explain the concept of a solution and the role of solvents in creating homogeneous mixtures, providing examples of solutions in everyday life.
Answer:
A solution is a homogeneous mixture formed when a solute, typically a solid, liquid, or gas, dissolves in a solvent to create a uniform composition at the molecular level. Solvents play a vital role in the formation of solutions by enabling the dispersion and even distribution of solute particles.
In everyday life, solutions are prevalent. An example is the simple process of making saltwater by dissolving salt in water. Here, salt acts as the solute, while water functions as the solvent, creating a saltwater solution. Additionally, the mixture of sugar in a cup of tea, where sugar is the solute and the tea serves as the solvent, results in a sweetened tea solution.
Solvents possess the ability to break the intermolecular forces in the solute, allowing solute particles to mix uniformly. This occurs as solvent molecules surround and separate solute particles, forming a stable and well-mixed solution. The molecular-level interactions between solute and solvent contribute to the overall homogeneity of the solution.
Understanding solutions is crucial in various fields, from chemistry to biology, as they play a fundamental role in numerous processes, including digestion, chemical reactions, and medication formulations. Overall, the concept of solutions and their prevalence in everyday scenarios highlight the importance of mixing substances to create a uniform and functional mixtures.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.