
separate
Definition
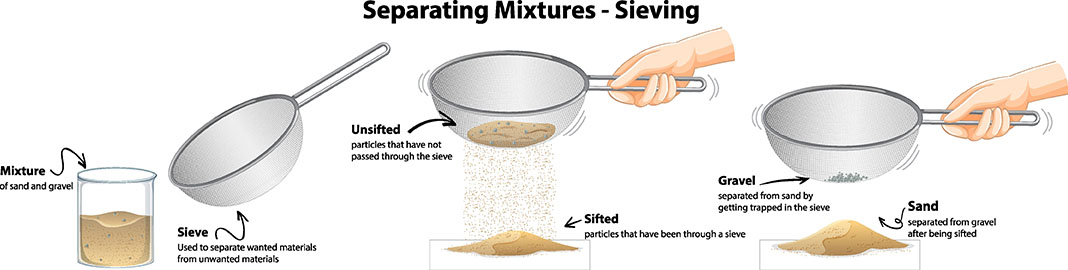
Separate means to keep things apart or distinct. In science, separation is often used to refer to the process of separating mixtures into their component parts.
There are many different methods of separation, each suited to a particular type of mixture. Some common methods of separation include:
- Filtration: This method is used to separate solids from liquids. A filter is used to trap the solids, allowing the liquid to pass through.
- Centrifugation: This method is used to separate liquids from solids or to separate mixtures of different densities. The mixture is spun in a centrifuge, causing the denser components to sink to the bottom and the less dense components to float to the top.
- Chromatography: This method is used to separate mixtures of different chemicals. The mixture is dissolved in a solvent and then passed through a column filled with a material that absorbs the different chemicals at different rates. This allows the chemicals to be separated into bands as they travel down the column.
Separation is a valuable tool in science. It allows scientists to study the properties of different materials and to identify the components of mixtures.
How can the word be used?
The problem can be separated into two parts.
Different forms of the word
Adjective:
- not joined or connected.
- kept apart from others.
- not combined or mixed.
Verb:
- to divide or keep apart.
- to set apart from others.
- to distinguish or differentiate.
Etymology
The word "separate" comes from the Latin word "separare", which means "to set apart".
The first recorded use of the word "separate" in English was in the 14th century.
The word "separate" is a Latin word, and it is related to the English word "separator".
Question
How can you separate mixed objects?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the process of chromatography and its significance in separating mixtures of substances, providing examples of real-world applications.
Answer:
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures of substances based on their differing affinities for a mobile phase (liquid or gas) and a stationary phase (solid or liquid). As the mixture is carried through the stationary phase by the mobile phase, individual components move at different rates, leading to their separation.
For example, paper chromatography involves placing a drop of a mixture on paper and immersing the paper in a solvent. As the solvent moves up the paper, it carries the mixture components with it. Substances that have a higher affinity for the paper stay lower, while those with a greater affinity for the solvent move higher.
Chromatography has diverse applications. In forensics, it's used to analyze ink or dye samples. Environmental scientists employ it to study pollution levels in water and air. In the pharmaceutical industry, chromatography is vital for purifying drugs. Additionally, it's used in food testing to detect additives or contaminants.
Chromatography's ability to separate complex mixtures with precision makes it an invaluable tool across various fields, contributing to research, quality control, and our understanding of the composition of substances in everyday life.