

Scientific diagrams are drawings or representations of objects or processes that are used to communicate scientific information. They are an essential part of the scientific process, as they can be used to:
The scientific diagram explained the process of photosynthesis.
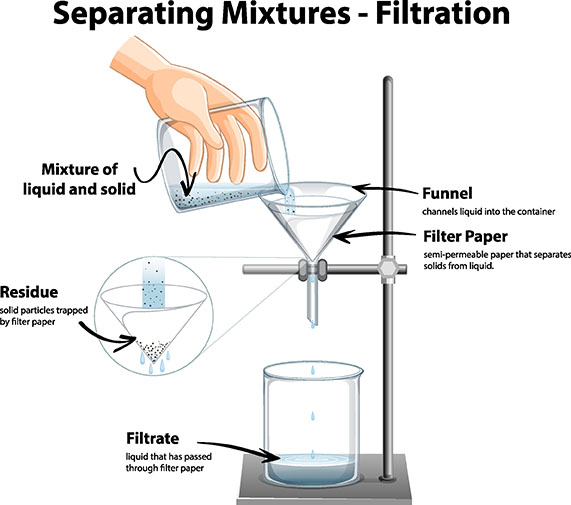
Noun:
Adjective:
The word "scientific diagram" is a compound word, consisting of the words "scientific" and "diagram".
The word "scientific" comes from the Latin word "scientificus", which means "of or relating to science".
The word "diagram" comes from the Greek word "diagramma", which means "drawing" or "sketch".
The first recorded use of the word "scientific diagram" in English was in the 19th century.
Why are scientific diagrams important?
Question:
Explain the purpose and key elements of a scientific diagram and how it enhances the communication of complex scientific concepts.
Answer:
A scientific diagram serves as a visual representation of complex ideas, structures, or processes, aiding in the clear communication of scientific concepts. It includes essential elements such as labelled components, scales, and explanatory annotations to convey information effectively.
Diagrams are especially valuable in situations where textual descriptions alone may be insufficient. For example, in biology, a diagram of a cell's organelles can provide a clearer understanding of its internal structure and functions than a lengthy written explanation. Similarly, in physics, a diagram illustrating the path of light rays through a lens can visually demonstrate how an image is formed.
The use of labels and annotations in scientific diagrams ensures that key features are identified and explained. Scales and proportions are included to provide accurate representations of size or quantity, aiding in comparisons and measurements. Arrows, lines, and shapes are often used to show relationships, processes, or movement.
Scientific diagrams transcend language barriers and offer a universal visual language that enhances comprehension and retention of complex information. They are particularly useful when teaching, presenting research findings, or conveying intricate concepts to a diverse audience, making scientific communication more accessible and engaging.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.