

Rubber is a natural or synthetic polymer with viscoelastic properties. This means that it is elastic (stretchy) and viscous (flows like a liquid). Rubber is made from the sap of rubber trees, or it can be synthesised from petroleum.
The properties of rubber are determined by its chemical composition and molecular structure. Natural rubber is made up of long chains of molecules called isoprene. These molecules are linked together by covalent bonds. Synthetic rubber is made up of different types of molecules, depending on the type of rubber.
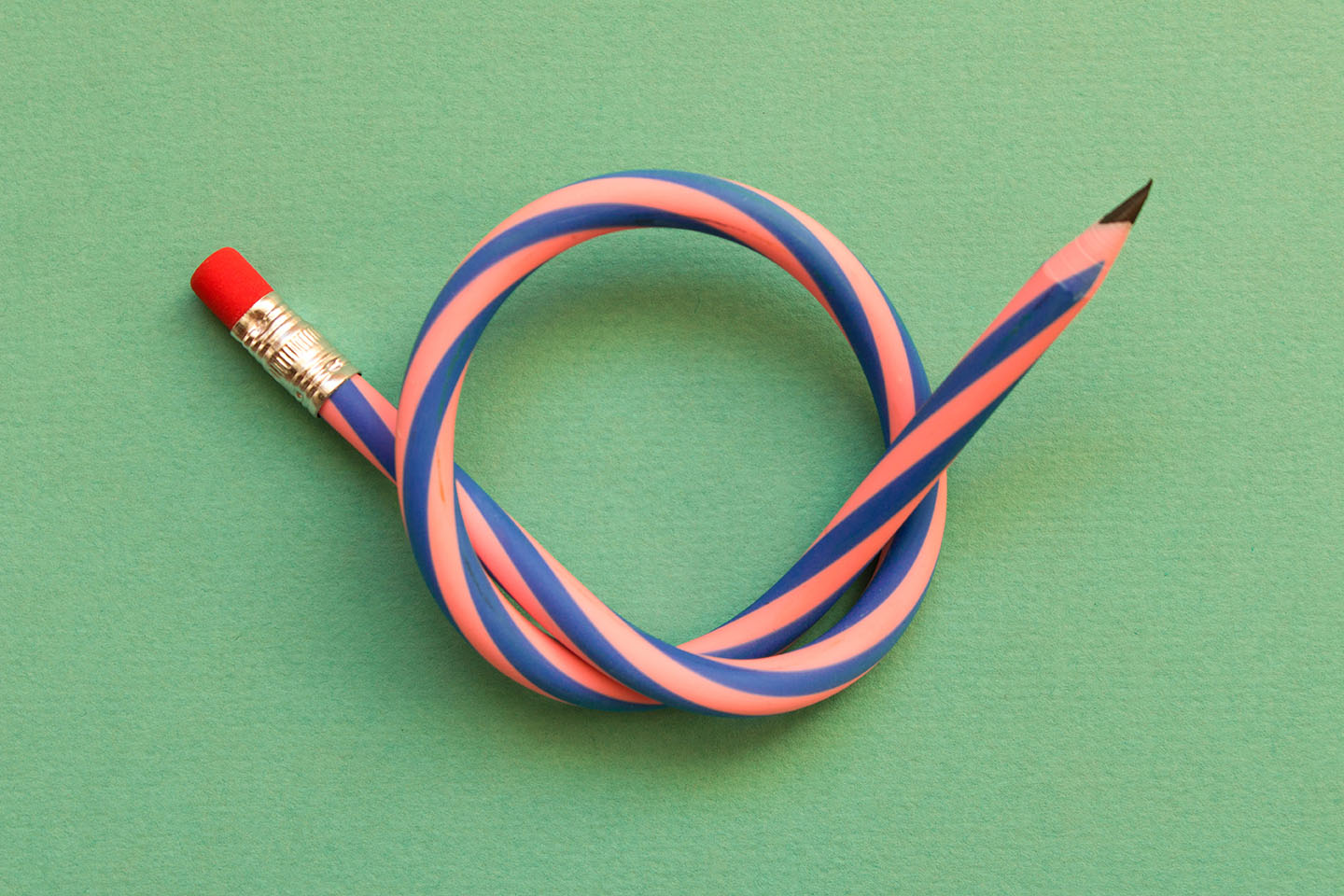
The elasticity of rubber is due to the way the molecules are arranged. The long chains of molecules are able to slide past each other when rubber is stretched. This allows the rubber to return to its original shape when the force is removed.
The viscosity of rubber is due to the interactions between the molecules. The molecules are attracted to each other, and this attraction prevents the rubber from flowing freely.
Rubber is used in many different applications because of its unique properties. It is used to make tires, balloons, gloves, and many other products. Rubber is also used in engineering applications, such as seals and gaskets.
The doctor gave me a rubber band to hold the bandage in place.
Noun:
Verb:
The word "rubber" comes from the Spanish word "caucho", which is derived from the Quechua word "kauchu", which means "tree sap".
The first recorded use of the word "rubber" in English was in the 16th century.
The word "rubber" is a cognate of the Dutch word "rubber" and the German word "Rübber", both of which mean "rubber".
The literal meaning of the word "rubber" is "something that rubs".
What things are made of rubber?
Question:
Discuss the properties and applications of rubber as a polymer, emphasising its importance in daily life and industrial sectors.
Answer:
Rubber, a versatile polymer, exhibits unique properties that make it invaluable in various applications. It is a natural or synthetic material with elasticity, flexibility, and resilience. The polymer chains in rubber can stretch and return to their original shape, providing these distinctive characteristics.
Rubber finds extensive use in everyday life and numerous industries. In consumer products, it's used for tires, footwear, gloves, and various accessories due to its excellent cushioning and shock-absorbing qualities. The automotive industry relies heavily on rubber for tires, contributing to vehicle performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
Industrial sectors like manufacturing and construction employ rubber for gaskets, seals, conveyor belts, and hoses due to its impermeability and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. The medical field also benefits from rubber-based materials in gloves, tubing, and medical devices, where its flexibility and biocompatibility are crucial.
Moreover, rubber plays a role in insulating electrical wires and cables, contributing to the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. Its thermal insulation properties are also exploited in industries dealing with extreme temperatures.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.