
rib cage
Definition
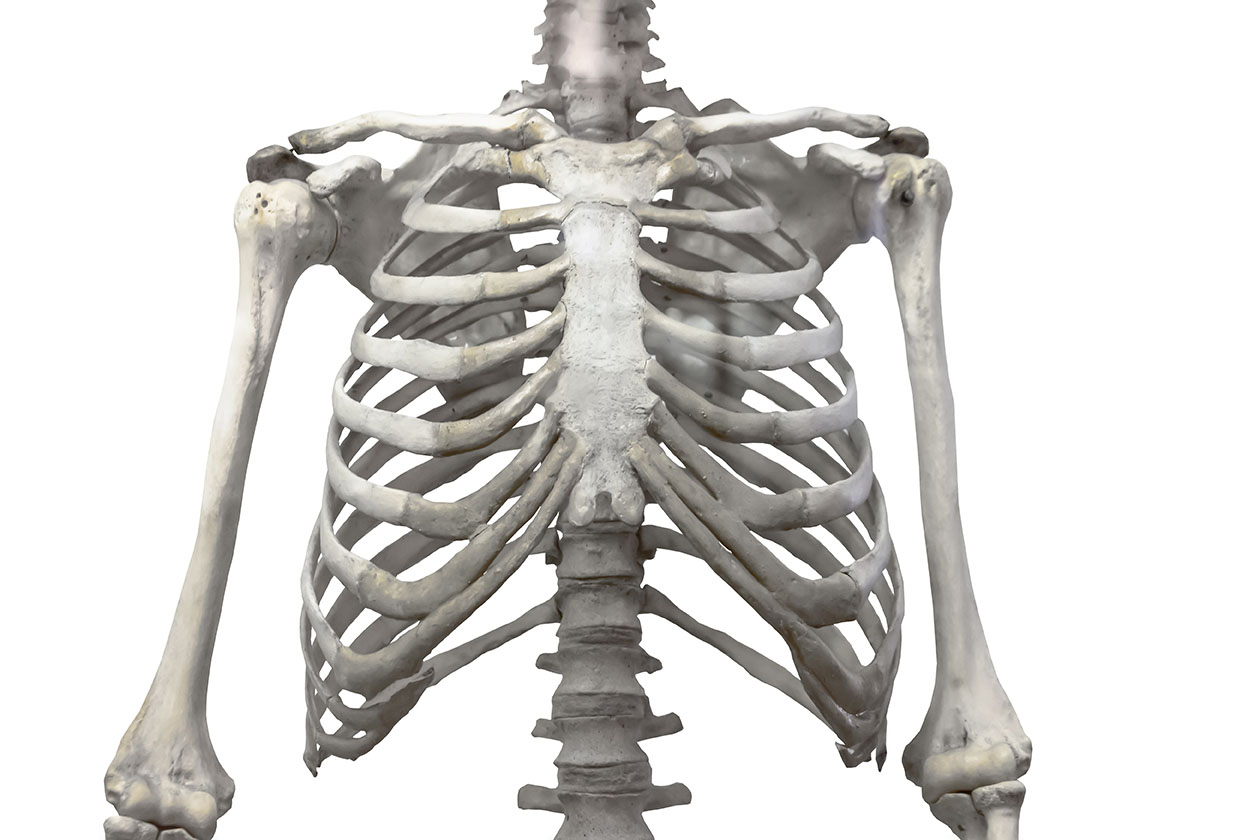
The rib cage is a structure of bones that surrounds and protects the thoracic cavity, which contains the heart, lungs, and other organs. It is made up of 24 bones, called ribs, which are connected to the sternum (breastbone) in the front and to the thoracic vertebrae (backbones) in the back.
The ribs are held together by muscles and ligaments, which allow them to move. When the ribs move, they expand and contract the thoracic cavity, which helps to move air in and out of the lungs.
The rib cage also protects the heart and lungs from injury. The curved shape of the rib cage helps to distribute the force of impact over a larger area, which helps to prevent the organs from being damaged.
The rib cage is also important for posture. The muscles that attach to the ribs help to keep the spine upright.
How can the word be used?
The rib cage is a structure of 24 bones that protect the heart and lungs.
Different forms of the word
Noun:
- the bony framework that protects the heart and lungs.
Etymology
The word "rib cage" comes from the Old English words "rib" and "cāg", which mean "rib" and "box" respectively.
The first recorded use of the word "rib cage" in English was in the 14th century.
The word "rib cage" is a compound word, made up of the words "rib" and "cage".
The Latin root word for "rib" is "costa", which means "rib".
The literal meaning of the word "rib cage" is "a cage made of ribs".
Question
Why is the rib cage important?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Describe the structure and function of the rib cage in the human body. Explain how the rib cage protects vital organs and aids in the process of respiration.
Answer:
The rib cage is a bony structure in the human body that consists of twelve pairs of ribs, a sternum (breastbone), and thoracic vertebrae in the spine. It encases and protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. Each rib is attached to the thoracic vertebrae in the back and the sternum in the front, forming a protective cage-like structure.
The primary function of the rib cage is to protect the internal organs within the thoracic cavity. The ribs act as a shield, absorbing and dispersing impact forces that could potentially harm the delicate structures beneath. The rib cage's protective role is crucial in safeguarding the heart and lungs, which are vital for the body's overall function.
Additionally, the rib cage plays a vital role in the process of respiration. During inhalation, the rib cage expands, allowing the lungs to fill with air. This expansion is facilitated by the movement of the ribs, which lift and create space for the lungs to expand. During exhalation, the rib cage returns to its original position, aiding in the expulsion of air from the lungs.