
rack and pinion
Definition
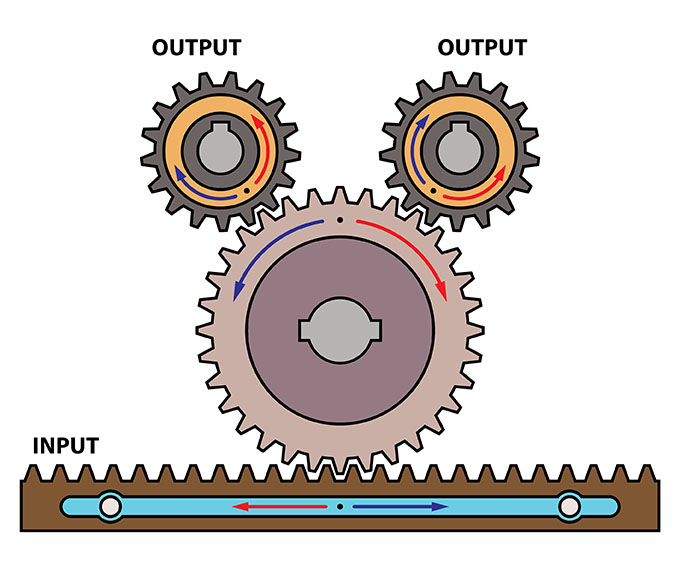
A rack and pinion is a mechanical linkage that converts rotary motion into linear motion. It is made up of two parts: a rack and a pinion. The rack is a straight bar with teeth on it. The pinion is a gear with teeth that fit into the teeth on the rack.
When the pinion turns, it moves the rack back and forth. The amount of movement of the rack is proportional to the amount of rotation of the pinion.
Rack and pinions are used in a variety of machines, including:
- Cars: Rack and pinion steering systems are used in most cars today. The steering wheel turns the pinion, which moves the rack and steers the car.
- Bicycles: Rack and pinion derailleurs are used to change gears on bicycles. The rider turns the shifter, which turns the pinion, which moves the rack and changes the gears.
- Power steering systems: Power steering systems use a rack and pinion to amplify the force of the driver's steering input. This makes it easier to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds.
Rack and pinions are a simple and efficient way to convert rotary motion into linear motion. They are used in a variety of machines because they are reliable and durable.
How can the word be used?
The clock's mechanism is powered by a rack and pinion gear train.
Different forms of the word
Noun: a system of gears that converts rotational motion into linear motion.
Adjective: of or relating to a rack and pinion system.
Etymology
The word "rack and pinion" comes from the Old English words "raca" and "pinna", which mean "toothed bar" and "pin" respectively.
The first recorded use of the word "rack and pinion" in English was in the 16th century.
Question
Where might you find a rack and pinion in use?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the working principle of a rack and pinion mechanism in simple terms and provide an example of its application in everyday objects.
Answer:
A rack and pinion mechanism is a simple mechanical system used to convert rotational motion into linear motion or vice versa. It consists of two main components: a gear-like component called a "pinion" and a flat, toothed bar known as a "rack." When the pinion gear is turned, it engages with the teeth on the rack, causing the rack to move in a straight line.
For instance, consider the steering system in a car. In this system, the circular motion of the steering wheel is transformed into the linear motion needed to turn the car's wheels. The steering wheel is connected to pinion gear, while a toothed rack is connected to the car's wheels. As the driver turns the steering wheel, the pinion gear engages with the rack, causing the rack to move left or right. This movement turns the wheels and changes the car's direction.
The rack and pinion mechanism is not only used in vehicles but also in various other applications like elevator systems, machinery, and even some hand tools. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice for converting between rotational and linear motion in a wide range of mechanical systems.