

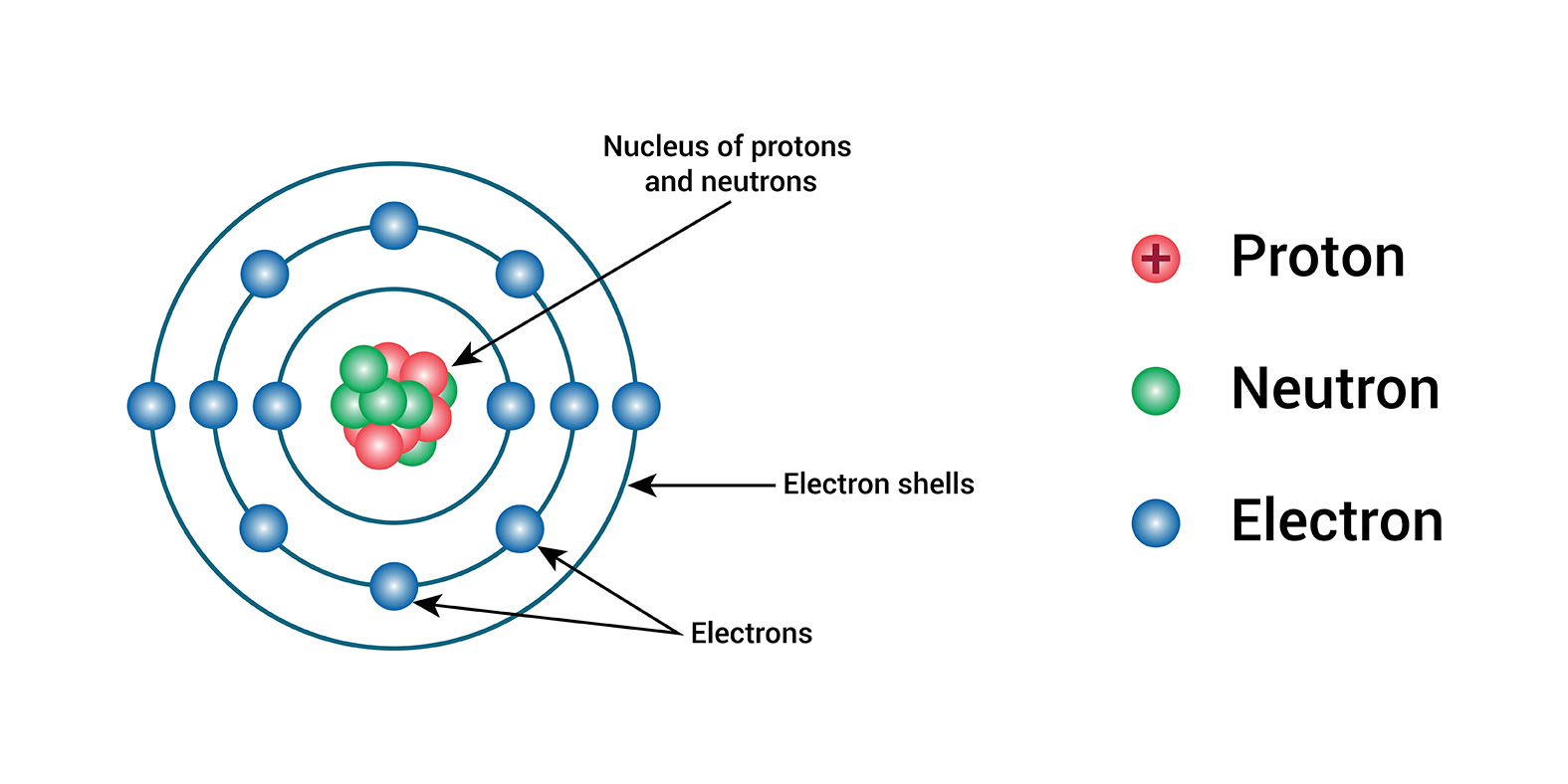
Protons are subatomic particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom. Protons have a positive charge, and they have a mass of 1.6726219 × 10^-27 kilograms. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. The atomic number of an element is unique, and it determines the chemical properties of the element.
Protons are held together in the nucleus of an atom by a strong force. The strong force is a very powerful force that acts over very short distances. It is the strong force that prevents protons from repelling each other due to their positive charges.
Protons are important because they help to determine the atom's mass and its chemical properties. They are also important in nuclear reactions, such as nuclear fusion and nuclear fission.
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is called the atomic number.
Noun: a subatomic particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of an atom.
Adjective: relating to a proton.
The word "proton" comes from the Greek word "protos", which means "first".
The first recorded use of the word "proton" in English was in 1920.
What is a proton?
Question:
Define a proton and explain its role in the structure of an atom. Discuss its electrical charge, location within the atom, and its significance in determining the element's identity.
Answer:
A proton is a subatomic particle found within the nucleus of an atom. It carries a positive electrical charge and is one of the fundamental constituents of matter.
The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. Protons contribute significantly to the atom's mass and are tightly bound within the nucleus due to strong nuclear forces.
Each element is defined by the number of protons it possesses, known as its atomic number. This number determines the element's unique identity. For instance, hydrogen has one proton, helium has two, and so on. The arrangement and number of protons in the nucleus dictate the chemical properties and behaviour of an element.
Protons carry a positive charge, which is balanced by the negative charge of electrons orbiting the nucleus. This balance of charges ensures that atoms are electrically neutral.