

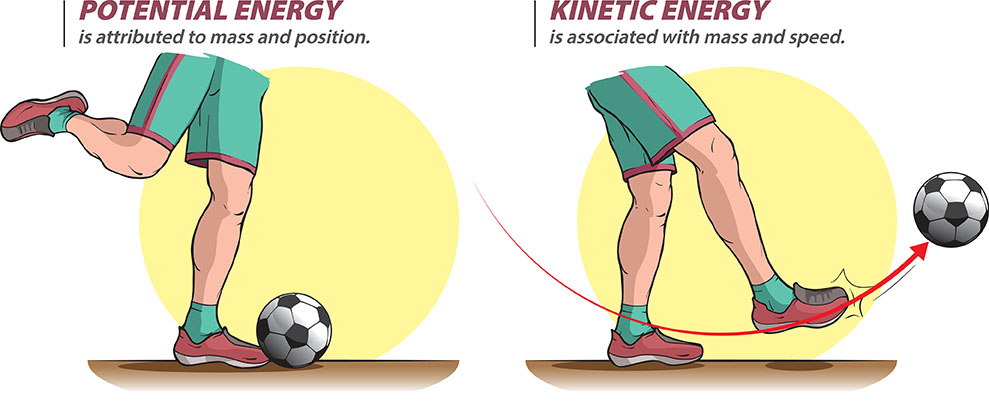
Potential energy is energy that is stored in an object because of its position or condition. It is the energy that an object has because of its position relative to another object, or because of its physical state.
Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. For example, when a ball is released from a height, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as it falls to the ground.
The amount of potential energy an object has depends on its mass, its height, and the strength of the force acting on it. For example, a ball that is held up higher has more potential energy than a ball that is held up lower.
Potential energy is an important concept in physics and engineering. It is used to explain how objects move, and it is used to design machines and structures.
The potential energy of a stretched spring is the energy it possesses because of its deformation.
Noun: the energy possessed by an object because of its position or state.
Adjective: relating to potential energy.
The word "potential energy" comes from the Latin word "potentia", which means "power". The word "potential" is an adjective that means "having the capacity to become or develop".
The first recorded use of the word "potential energy" in English was in the early 19th century.
What is potential energy?
Question:
Explain the concept of potential energy and provide examples of everyday situations where potential energy is demonstrated. Discuss the relationship between height, mass, and potential energy, and how potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy.
Answer:
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or condition. It's the energy that can be converted into kinetic energy (energy of motion) when the object's position changes.
Everyday situations illustrate potential energy. For instance, a book held above the ground has potential energy due to its height. Similarly, a stretched rubber band or a compressed spring stores potential energy. Water stored in a dam has gravitational potential energy due to its elevation.
The relationship between height, mass, and potential energy is described by the formula PE = mgh, where PE is potential energy, m is mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is height. An object's potential energy increases with mass and height.
Potential energy can be converted into other forms. For example, as the book falls, potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. A stretched rubber band releases potential energy as it returns to its original shape. In hydropower plants, potential energy in elevated water is converted into kinetic energy as it falls, generating electricity.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.