

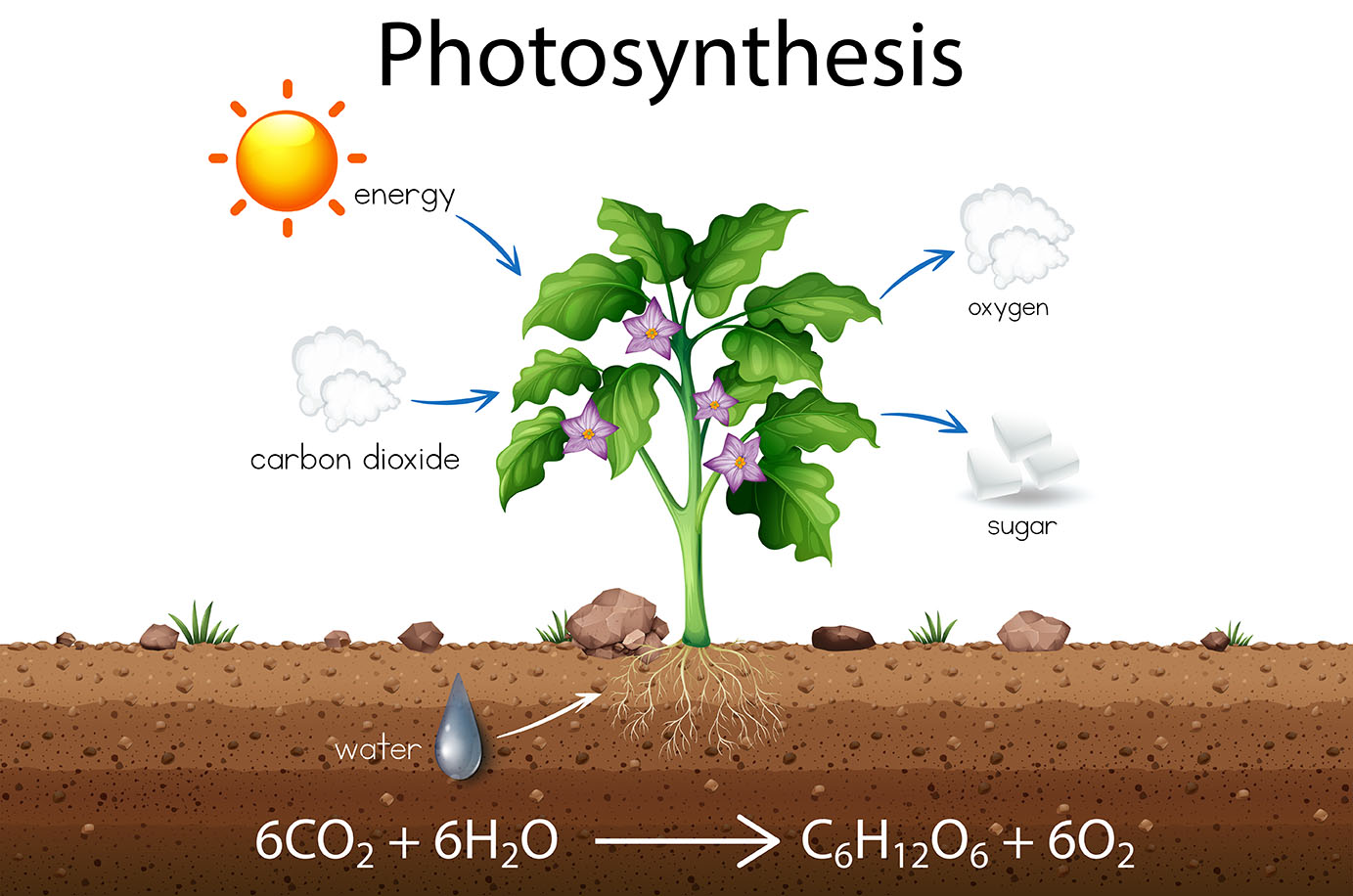
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates. Photosynthesis is the process by which almost all life on Earth obtains energy.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In light-dependent reactions, sunlight is used to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is then used to create ATP, a molecule that stores energy. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
In the Calvin cycle, ATP and hydrogen are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Glucose is a sugar that can be used by cells for energy or stored for later use.
Photosynthesis is a complex process that requires many different molecules and reactions. However, the basic steps of photosynthesis are the same for all organisms that photosynthesise.
Photosynthesis is an essential process for life on Earth. It provides the food and oxygen that all living things need to survive. Photosynthesis is also responsible for the cycling of carbon and water in the biosphere.
Plants use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into food.
Noun:
Adjective:
The word "photosynthesis" comes from the Greek words "phōs" (light) and "synthesis" (putting together).
The word "photosynthesis" was first used in English in the 19th century. It was used to refer to the process by which plants use sunlight to make food.
The word "photosynthesis" is a compound word, made up of the words "photo" and "synthesis". The word "photo" comes from the Greek word "phōs", which means "light". The word "synthesis" comes from the Greek word "synthesis", which means "putting together".
So, photosynthesis literally means "putting together with light". This is a reference to the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich carbohydrates.
What is photosynthesis?
Question:
Explain the process of photosynthesis and its significance in the ecosystem. Describe how plants capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy, highlighting the role of chlorophyll in this process.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that allows plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, primarily in the form of glucose. It is essential for both plants and the ecosystem. During photosynthesis, plants capture sunlight using pigments like chlorophyll, which are found in chloroplasts within plant cells.
Chlorophyll absorbs light in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, while reflecting green light, which is why plants appear green to our eyes. This absorbed light energy is used to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct, and generating ATP, a molecule that stores energy. ATP powers the conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of biochemical reactions known as the Calvin cycle.
Photosynthesis has far-reaching significance. It's the basis of the food chain, as plants produce their own energy-rich food, which is then consumed by herbivores and further up the trophic levels. Oxygen released during photosynthesis is essential for the respiration of both plants and animals.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.