
phloem
Definition
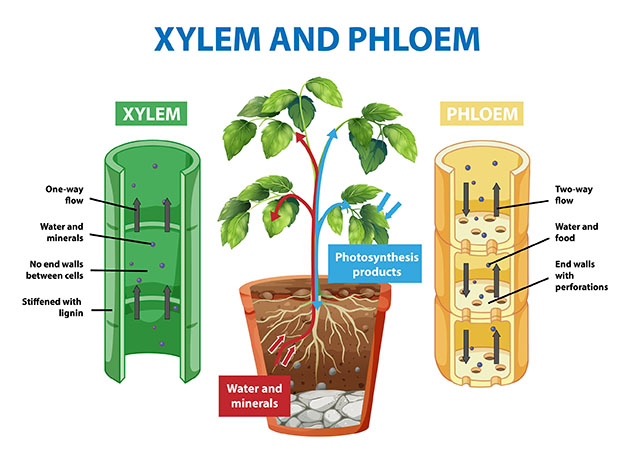
Phloem is a type of tissue in plants that transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. It is made up of long, thin cells that are connected end to end. The cells in the phloem are alive and have cytoplasm, which is the jelly-like substance that makes up cells.
Phloem is found in the vascular tissue of plants, which is also made up of xylem. The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves. Phloem and xylem work together to transport the resources that plants need to grow and survive.
How can the word be used?
The phloem is the tissue that transports food in plants.
Different forms of the word
Noun:
- phloem (the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as photosynthates, in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant).
- phloem fibre (a type of fibre that is found in the phloem).
Adjective:
- phloem (of or relating to the phloem).
Etymology
The word "phloem" comes from the Greek word "phloios", which means "bark". The word "phloem" was first used in English in the 19th century.
The phloem is a tissue that transports food made in the leaves during photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant. It is made up of sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem fibres. Sieve tubes are the main cells of the phloem. They are long, thin cells that are connected end to end. Companion cells are smaller cells that are found next to the sieve tubes. They help to support the sieve tubes and transport nutrients. Phloem fibers are strong, supportive cells that are found in the phloem.
Question
What is phloem?