

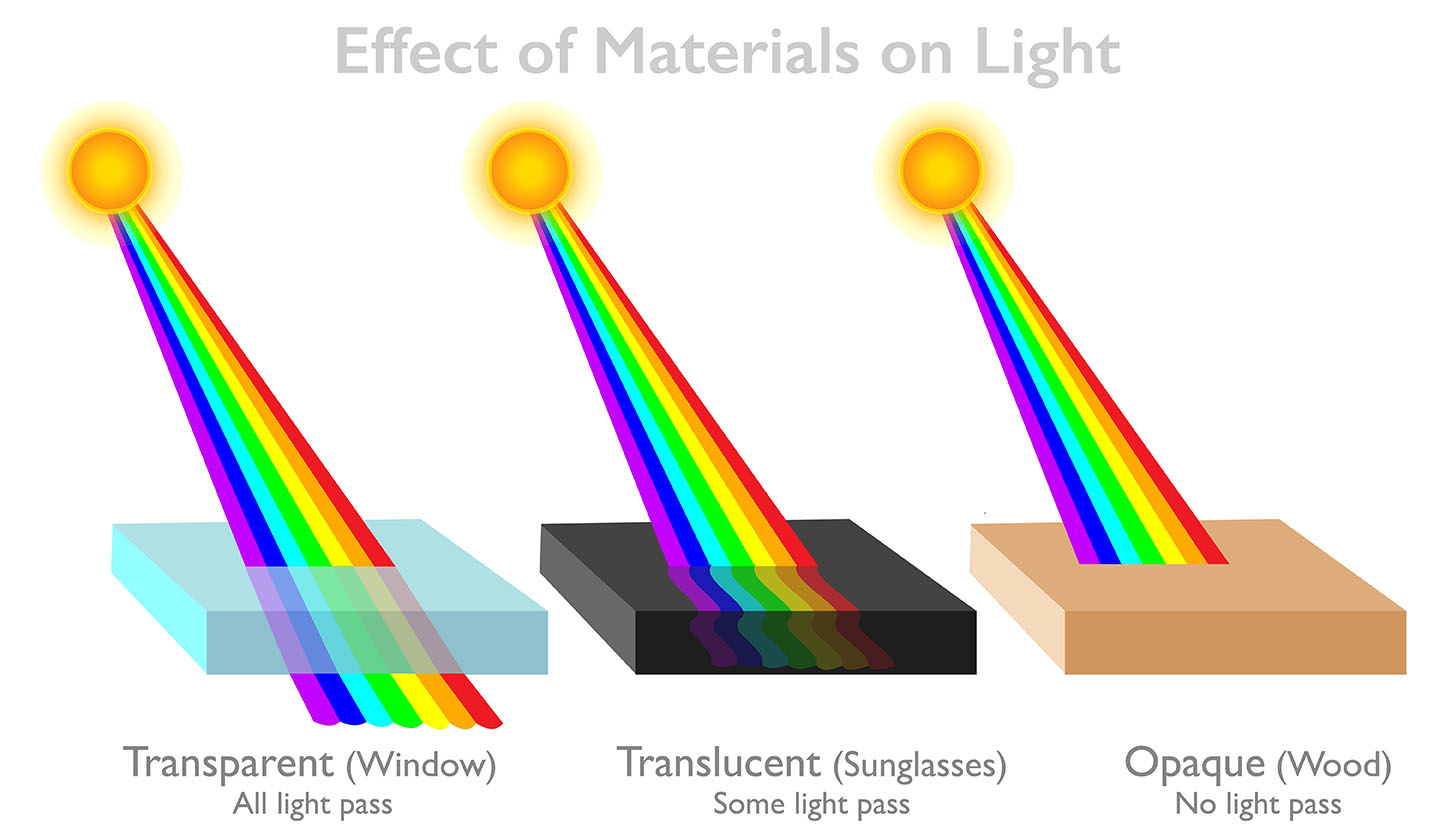
Opaque is a term used to describe a material that does not allow light to pass through it. Opaque materials reflect or absorb all of the light that hits them.
Opaque materials are made up of atoms that are tightly packed together. This makes it difficult for light to pass through the material. The light is either reflected back off of the surface of the material or absorbed by the atoms in the material.
Some common examples of opaque materials include metals, plastics, and wood. Metals are opaque because their atoms are tightly packed together. Plastics are opaque because they are made up of long chains of molecules that are also tightly packed together. Wood is opaque because its cells are tightly packed together.
Opaque materials are important in many different ways. They are used to make buildings, furniture, and other objects. They are also used in the construction of telescopes and other optical instruments.
Opaque objects can be found in many different contexts, such as in windows, walls, and clothing.
Adjective: Not allowing light to pass through.
Noun: Something that is not transparent.
The word "opaque" comes from the Latin word "opacus," which means "dark" or "hidden." The Latin word "opacus" is also the source of the French word "opaque" and the Italian word "opaco.".
The word "opaque" was first used in English in the 16th century. It was used to refer to something that was not transparent.
What is the opposite of opaque?
Question:
Explain what is meant by the term "opaque" in the context of materials and light, and provide an example of an opaque substance.
Answer:
In the context of materials and light, the term "opaque" refers to a substance or material that does not allow light to pass through it. When light encounters an opaque material, it is either absorbed or reflected, resulting in the material appearing solid and not transmitting any light through it.
An example of an opaque substance is wood. When light shines on a wooden surface, it does not pass through the material but is instead either absorbed by the wood or reflected off its surface. This lack of transparency makes wood an opaque material. Other examples of opaque substances include metals like iron and non-transparent plastics.
The opacity of materials is determined by their molecular and atomic structure, which affects how they interact with light. Opaque materials are commonly used in various applications where blocking light is essential, such as building materials, containers, and screens. Understanding the properties of opaque materials is crucial for designing objects that control the passage of light based on their intended use.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.