

A microbe is a microscopic organism that can be found in all parts of the environment. Microbes include bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, and viruses.
Microbes are very diverse and come in all shapes and sizes. Some microbes are single-celled, while others are multicellular. Some microbes are free-living, while others live in association with other organisms.
Microbes play an important role in the environment. They are involved in the cycling of nutrients, the decomposition of organic matter, and the production of food. Microbes can also be used to produce biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other products.
Some microbes can cause disease. These microbes can enter the body through the air, water, food, or contact with an infected person or animal. Diseases caused by microbes can range from mild to severe, and some can even be fatal.
It is important to understand microbes and how they can affect our health. We can protect ourselves from disease by practising good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and eating a healthy diet.
The infection was caused by a microbe.
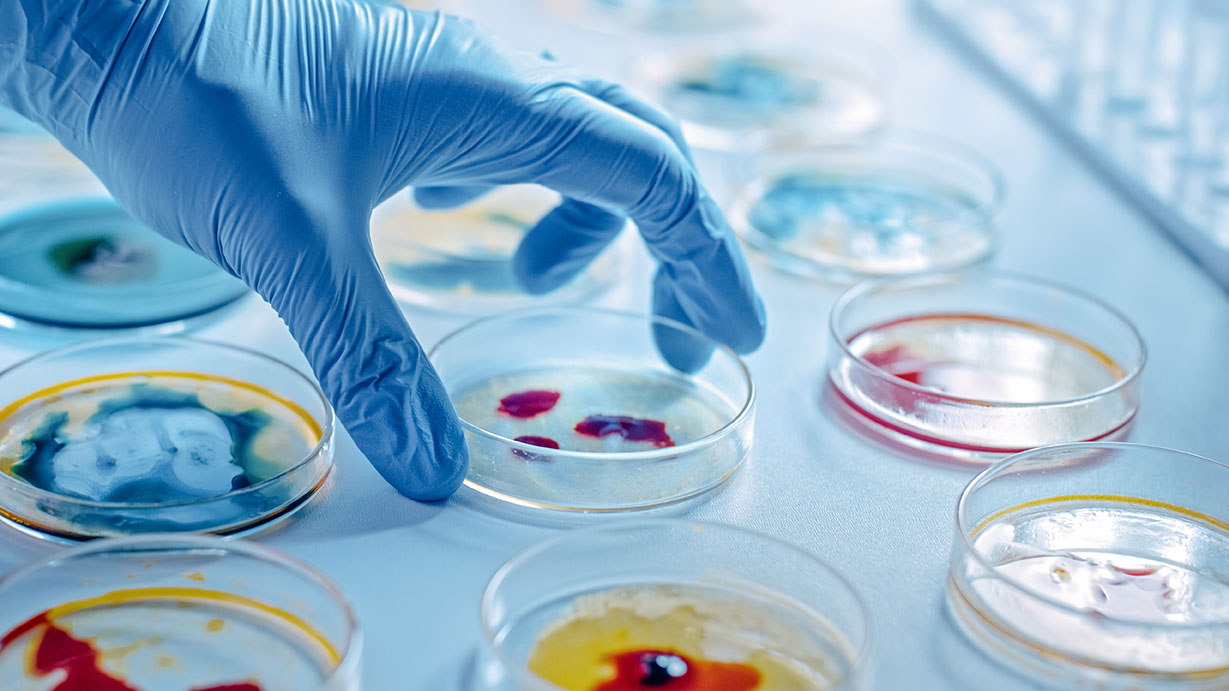
Noun: A very small organism that can only be seen with a microscope.
Adjective: Relating to or caused by microbes.
Verb: To infect or contaminate with microbes.
The word "microbe" comes from the Greek words "mikros" (small) and "bios" (life). The word "microbe" was first used in English in the 19th century.
The literal meaning of the word "microbe" is "small life". This is because microbes are very small organisms that can only be seen with a microscope.
What is a microbe?
Question:
Explain the role of microbes in the environment and their impact on human health.
Answer:
Microbes, also known as microorganisms, are tiny living organisms that play significant roles in various ecosystems and have profound effects on human health. Despite their small size, microbes have a vast impact on both the environment and our well-being.
In the environment, microbes are essential for nutrient cycling and decomposition. They break down organic matter, recycling nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, which are vital for plant growth and ecosystem balance. Additionally, certain microbes can form symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding in nutrient uptake and enhancing soil fertility.
Microbes also influence human health, both positively and negatively. Beneficial microbes, such as the ones residing in our gut (gut microbiota), aid in digestion, and vitamin synthesis, and even play a role in our immune system. However, harmful microbes, known as pathogens, can cause diseases ranging from common infections to more serious illnesses.
Understanding and managing microbial ecosystems is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and human health. Advances in microbiology allow us to harness the benefits of microbes, such as using them in bioremediation to clean up polluted environments, while also developing strategies to combat microbial diseases.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.