

Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms to maintain life. It is the process by which organisms obtain energy from food and use it to grow, reproduce, and maintain their body functions.
Metabolism is divided into two main types: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism is the process of breaking down molecules into smaller molecules, releasing energy in the process. Anabolism is the process of building up molecules from smaller molecules, requiring energy.
The rate of metabolism is affected by a number of factors, including age, sex, body composition, temperature, and activity level. Metabolism is generally slower in children and older adults, and it is faster in men than in women. People with more muscle mass have a higher metabolic rate than people with less muscle mass.
Metabolism is important for a number of reasons. It provides the energy that organisms need to function. It also helps to maintain body temperature and to remove waste products from the body.
Metabolism can be affected by a number of factors, including diet, exercise, and medications. A healthy diet and regular exercise can help to boost metabolism. Some medications can also affect metabolism, so it is important to talk to your doctor if you are taking any medications that may affect your metabolism.
A high metabolism can help you lose weight.
Noun: The set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms to maintain life.
Adjective: Relating to metabolism.
Verb: To metabolise.
The word "metabolism" comes from the Greek words "metabolē" (change) and "metaballein" (to change). The word "metabolism" was first used in English in the 17th century.
The literal meaning of the word "metabolism" is "change of matter". This is because metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms to convert food into energy and to build up and break down molecules.
What is a metabolism?
Question:
Explain the concept of metabolism in living organisms and its significance in maintaining life processes. Provide examples of metabolic reactions and discuss how metabolism is regulated to ensure the proper functioning of cells and organisms.
Answer:
Metabolism refers to the sum of all chemical reactions occurring within living organisms to maintain life processes. These reactions are vital for energy production, growth, and the maintenance of cellular structures. Metabolism can be divided into two main categories: catabolism and anabolism.
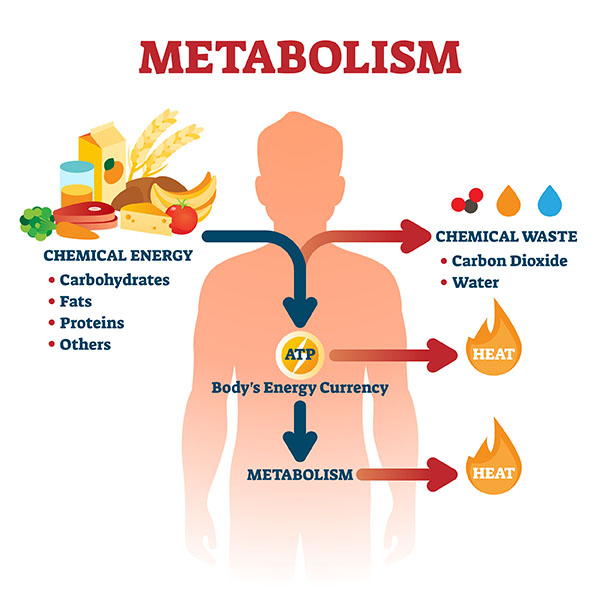
Catabolic reactions involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy. An example is cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water to produce ATP, the energy currency of cells. Anabolic reactions, on the other hand, build complex molecules from simpler ones, consuming energy. Protein synthesis, using amino acids to construct proteins, is an example of an anabolic process.
Metabolism is carefully regulated to ensure optimal cellular function. Enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing metabolic reactions, and their activity is regulated by various factors, including temperature and pH. Additionally, hormones like insulin and glucagon regulate metabolism by controlling blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, metabolism is essential for the survival of living organisms. It enables the extraction of energy from nutrients, the synthesis of necessary molecules, and the maintenance of cellular processes. The intricate balance between catabolic and anabolic reactions, along with enzyme and hormone regulation, ensures that metabolism operates efficiently to sustain life.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.