

A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk. It is found in female mammals, and it is responsible for feeding their young.
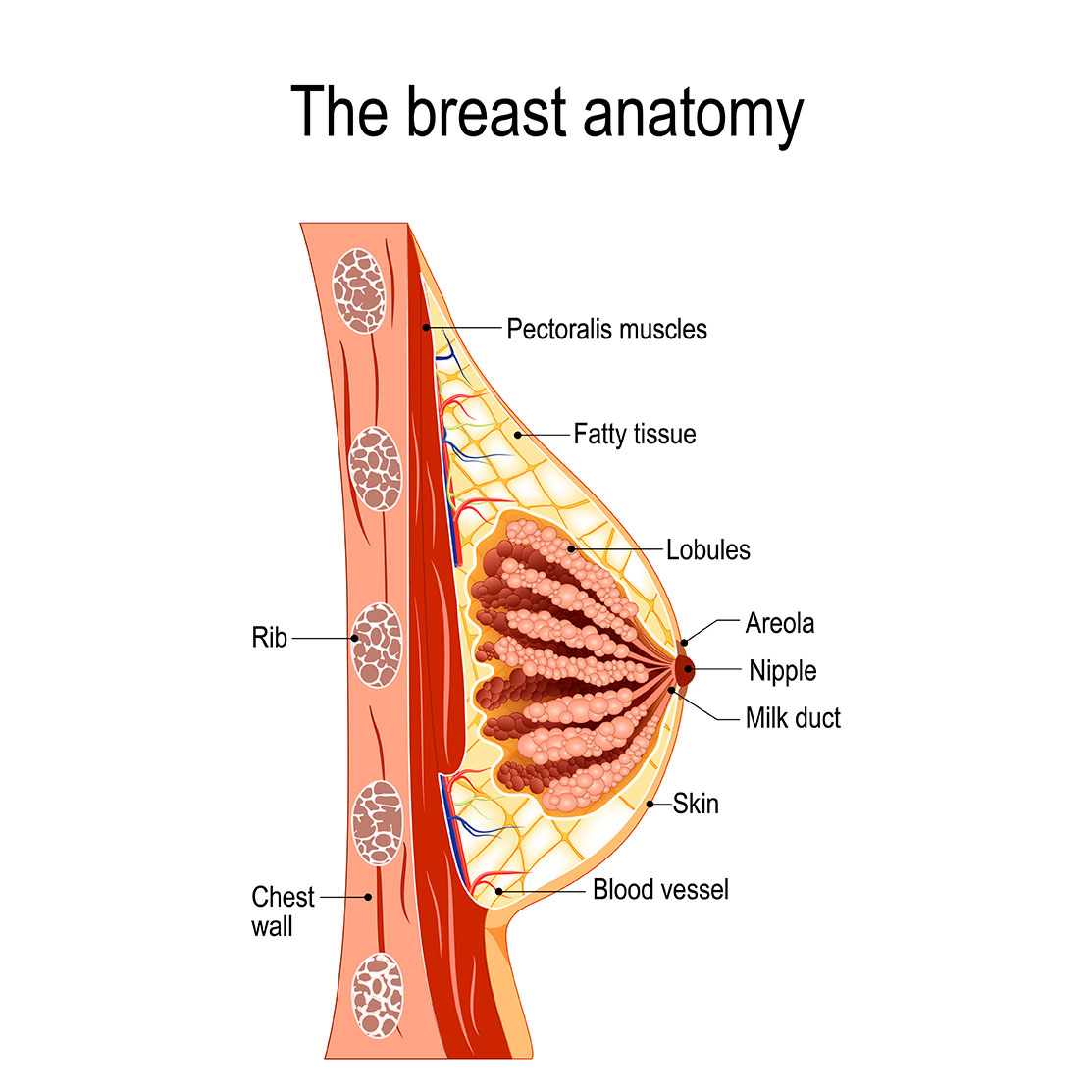
Mammary glands are made up of lobules, which are small sacs that produce milk. The lobules are connected to ducts, which carry the milk to the nipples.
The milk produced by mammary glands is a complex liquid that contains nutrients, antibodies, and other substances that are essential for the development of the young mammal. The composition of milk varies depending on the species of mammal and the stage of lactation.
Mammary glands are stimulated to produce milk by the hormone prolactin. Prolactin is released from the pituitary gland in response to suckling. Suckling also stimulates the release of oxytocin, which causes the milk to be released from the ducts.
Mammary glands are an important part of the reproductive system of female mammals. They allow mammals to provide their young with the nutrients and antibodies they need to survive and thrive.
Mammary gland cancer is a common cancer in women.
Noun: An organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed their young.
Adjective: Describing something that is related to mammary glands. For example, you could say "mammary gland cancer" or "mammary gland tissue".
The word "mammary gland" comes from the Latin words "mamma", which means "breast", and "glandula", which means "gland". This is a reference to the fact that mammary glands are located in the breasts of female mammals.
The word "mammary gland" was first used in English in the 17th century. It was originally used to describe the glands that produce milk in female mammals, but it soon came to be used in a more general sense to describe any gland that produces milk.
What is a mammary gland?
Question:
Explain the function of a mammary gland in mammals and its importance in the survival of offspring.
Answer:
A "mammary gland" is a specialised organ found in female mammals that plays a crucial role in nurturing their young. Its primary function is to produce milk, a nutrient-rich fluid that provides essential nourishment to newborn offspring. The mammary gland undergoes significant development during pregnancy, and after birth, it starts producing milk to feed the young.
The importance of mammary glands in the survival of offspring cannot be overstated. Milk produced by these glands is an ideal source of nutrients, including proteins, fats, sugars, vitamins, and antibodies. This rich and balanced composition supports the rapid growth and development of newborns, ensuring their well-being during the early stages of life when they are most vulnerable.
Milk also contains antibodies that help boost the immune systems of newborns, protecting them from various infections and diseases. This transfer of immunity from mother to offspring through milk is a crucial survival strategy in many species.
In conclusion, mammary glands are specialised structures in female mammals that produce milk, a vital source of nutrients and immunity for their offspring. This remarkable adaptation ensures the successful development and survival of young mammals during their early stages of life.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.