

Magnetic north is the direction that a compass needle points to. It is not the same as the true north, which is the direction of the North Pole.
The Earth has a magnetic field, and the magnetic needle in a compass is attracted to the north and south poles of the Earth's magnetic field. The north pole of the magnetic needle is attracted to the south pole of the Earth's magnetic field, and the south pole of the magnetic needle is attracted to the north pole of the Earth's magnetic field. This is why the magnetic needle always points north.
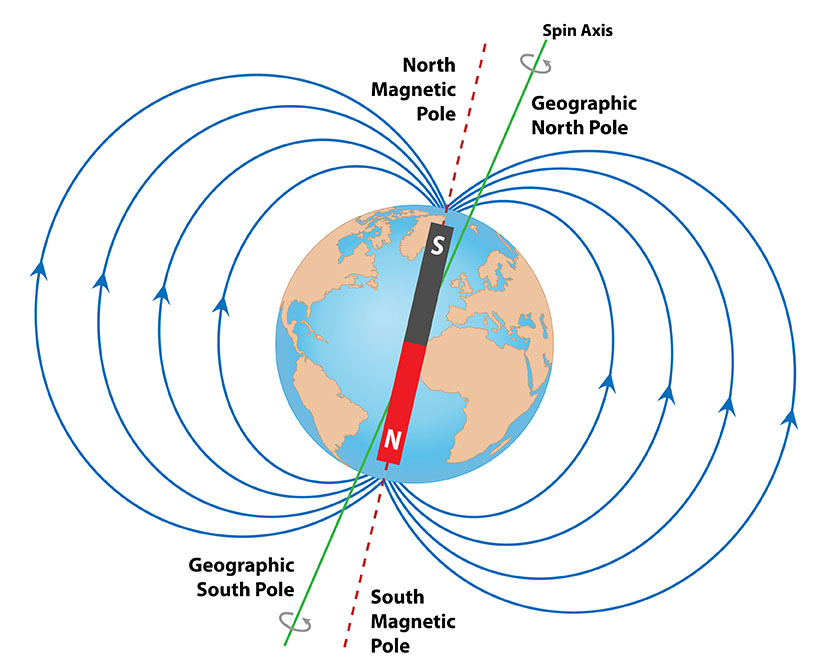
However, the Earth's magnetic field is not perfectly aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation. This means that magnetic north is not the same as true north. The difference between magnetic north and true north is called magnetic declination.
Magnetic declination is caused by the fact that the Earth's magnetic field is constantly changing. The Earth's magnetic poles are slowly moving, and the strength of the Earth's magnetic field is also changing. This means that magnetic declination is different for different points in time and different locations on the Earth.
Magnetic declination can be corrected by using a compass that has a declination adjustment. This adjustment will allow you to read the compass and get an accurate direction to true north.
The ship was sailing on a course of magnetic north.
Noun: The direction that a compass needle points to, which is not exactly the same as true north because the Earth's magnetic field is not perfectly aligned with its axis of rotation.
Adjective: Describing something that is related to magnetic north. For example, you could say "magnetic north pole" or "magnetic north deviation".
The word "magnetic north" comes from the noun "magnetic", which describes something that has the properties of a magnet, and the noun "north", which is the direction that is at a right angle to both east and west.
The word "magnetic north" was first used in English in the 17th century. It was originally used to describe the direction that a compass needle pointed to, but it soon came to be used in a more general sense to describe any direction that is aligned with the Earth's magnetic field.
What is magnetic north?
Question:
Explain the concept of magnetic north and its importance in navigation. How does magnetic north differ from geographic north?
Answer:
Magnetic north is a key concept in navigation, serving as a reference point for determining directions using a magnetic compass. It is the point on the Earth's surface towards which the north-seeking pole of a magnetic needle points. This magnetic north is different from the geographic north pole, which is the northernmost point on the Earth's rotational axis.
The Earth's core generates a magnetic field, similar to that of a bar magnet, which has its own north and south poles. These magnetic poles are not aligned with the planet's geographic poles. The magnetic north pole is located in the Arctic region, near Canada, but it's important to note that it is not fixed and can shift over time due to changes in the Earth's molten iron core.
The difference between magnetic north and geographic north is known as magnetic declination. This angular difference varies based on one's location on Earth's surface. Navigators need to account for this variation to ensure accurate navigation. For instance, in some places, a magnetic compass pointing to the magnetic north would not align with true north on a map.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.