

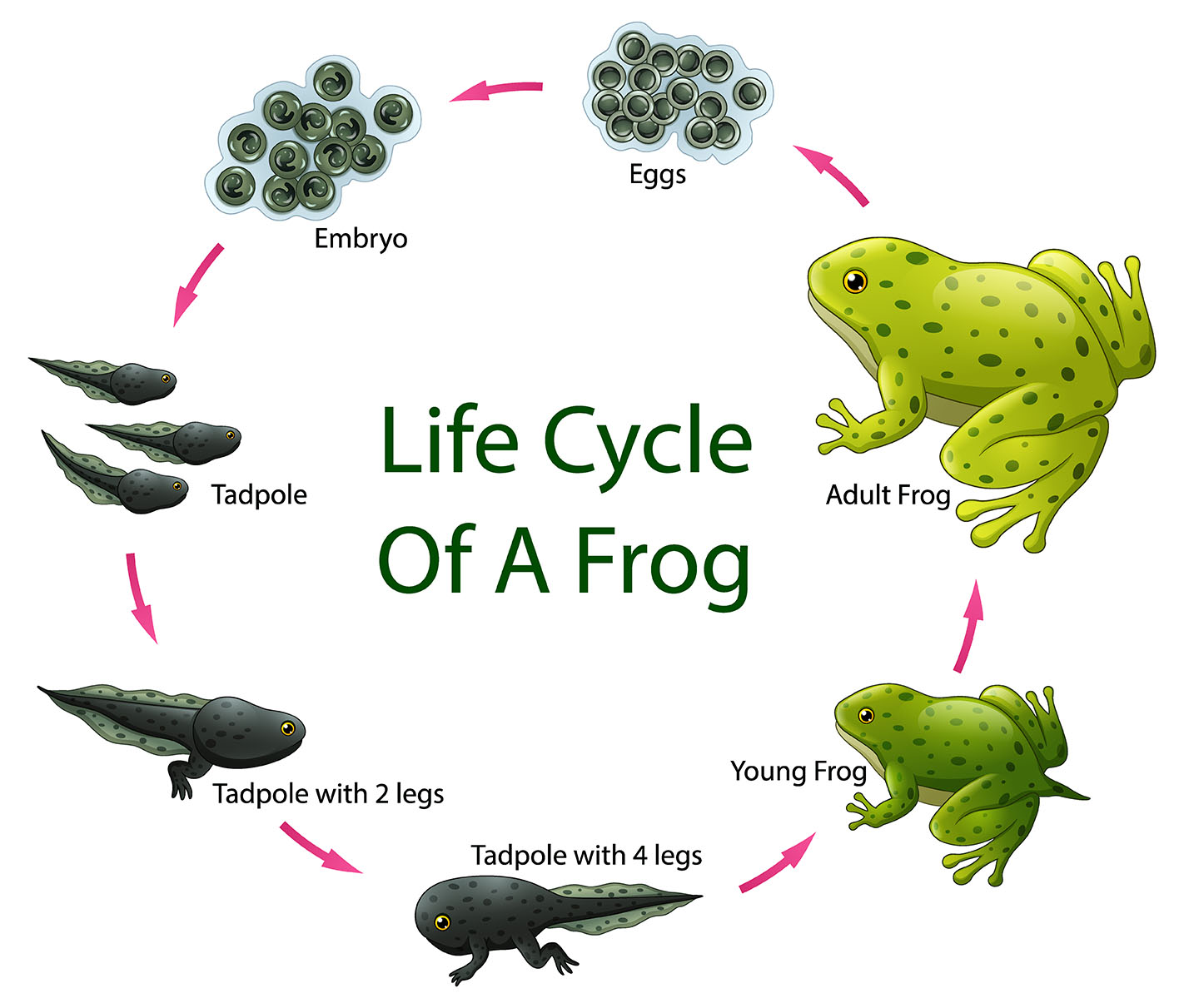
A life cycle is the sequence of stages that a living thing goes through from conception to death. The stages of a life cycle are usually divided into four main parts:
The stages of a life cycle can vary depending on the organism. For example, the life cycle of a human is much longer than the life cycle of a butterfly. Humans typically live for about 80 years, while butterflies only live for about a few weeks.
The life cycle of an organism is important because it helps to ensure the survival of the species. By reproducing, organisms pass on their genes to their offspring. This helps to ensure that the species will continue to exist.
The life cycle of a product typically lasts for about five years.
Noun: Life cycle is the stages that an organism goes through from birth to death. It includes the stages of growth, reproduction, and death.
Adjective: Life-cycle is an adjective that describes something that relates to the life cycle of an organism. For example, a life-cycle diagram is a diagram that shows the stages of the life cycle of an organism.
Verb: To life-cycle is to go through the stages of the life cycle. For example, a plant life-cycles through the stages of germination, growth, flowering, and reproduction.
The word "life cycle" comes from the Old English words "life" and "cicle", which mean "course of events". It was first used in English in the 14th century.
The Old English word "life" comes from the Proto-Germanic word *leif, which also means "life".
The Old English word "cicle" comes from the Proto-Germanic word *kīkilaz, which also means "course of events".
So, the word "life cycle" literally means "course of events of life".
What is a life cycle?
Question:
Explain the concept of a life cycle and provide an example of a life cycle in the animal kingdom. How does the understanding of life cycles contribute to our understanding of nature and the environment?
Answer:
A life cycle refers to the series of stages that an organism goes through from its birth or creation to its eventual death or cessation. This sequence typically involves growth, reproduction, and eventually leading to the birth of the next generation. Understanding life cycles provides insights into the developmental changes and adaptations that occur in an organism's lifetime.
A classic example of a life cycle in the animal kingdom is that of the butterfly. The cycle begins with an egg, which hatches into a caterpillar. The caterpillar undergoes several moults and stages of growth, eventually forming a chrysalis. Inside the chrysalis, the metamorphosis takes place, resulting in the emergence of a butterfly. This butterfly then continues the cycle by laying eggs and starting the process anew.
The understanding of life cycles is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of species and their environments. It helps scientists and ecologists study the intricate relationships between organisms, their predators, prey, and habitats. This knowledge aids in making informed conservation decisions and understanding the impact of environmental changes on various species. Additionally, comprehending life cycles assists in agricultural practices, pest control, and the management of resources. Overall, the study of life cycles enhances our understanding of the intricate web of life on Earth and the importance of maintaining ecological balance.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.