

In biology, a larva is the non-feeding, typically worm-like, first stage in the development of an insect, mite, or other arthropod. Larvae are distinguished from nymphs, which are juvenile stages that closely resemble the adult, and pupae, which are juvenile stages that are enclosed in a hard case.
Larvae typically have different body plans than adults. For example, larvae of insects often have chewing mouthparts, while adults have sucking mouthparts. Larvae of butterflies and moths have six legs, while adults have four legs.
Larvae usually eat a lot and grow quickly. They moult their skin several times as they grow. After the last moult, the larva becomes an adult insect.
The larva stage is an important part of the insect life cycle. It is during this stage that the insect grows and develops its adult features. The larva stage also helps the insect to disperse to new areas.
Larvae feed on a variety of different foods, depending on the species of insect.
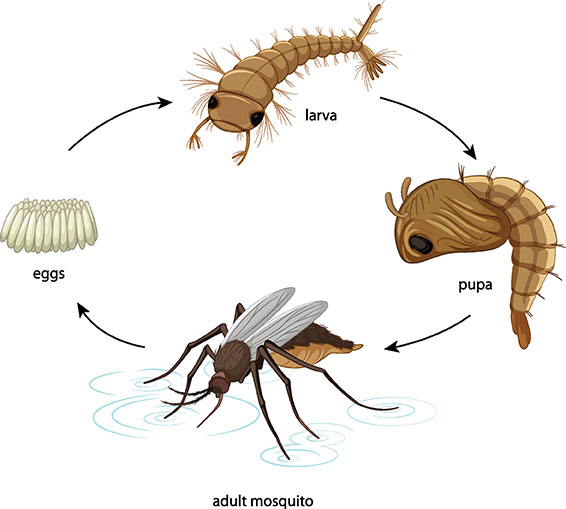
Noun: Larva is the immature form of an insect, typically wingless and worm-like.
Adjective: Larval is an adjective that describes something that is related to a larva. For example, a larval stage is a stage in the life cycle of an insect when it is a larva.
Verb: To larvate is to undergo the larval stage. For example, a butterfly larvates when it transforms into a pupa.
The word "larva" comes from the Latin word "larva", which means "mask" or "ghost". This is because larvae often have a very different appearance from the adult insects that they will eventually become.
The Latin word "larva" is thought to be related to the Greek word "λάρβα" (larva), which also means "mask" or "ghost".
What is larva?
Question:
Explain the life cycle of an insect, focusing on the larval stage. How does the larval stage contribute to the growth and development of insects?
Answer:
The life cycle of an insect typically involves several distinct stages, with the larval stage being a crucial part of this process.
During the larval stage, an insect undergoes significant growth and development. Larvae are usually the juvenile, worm-like form of insects that hatch from eggs. This stage serves primarily for feeding and growth, enabling the insect to accumulate the necessary energy and nutrients to transition into the next stage of its life cycle.
Larvae often have specialised feeding structures that allow them to consume specific types of food sources. Their rapid feeding and growth help them increase in size, shedding their exoskeleton periodically in a process called moulting. Moulting allows them to accommodate their expanding body and continue growing.
For instance, in the case of butterflies, the larval stage is known as a caterpillar. During this stage, the caterpillar feeds voraciously on plant leaves, storing energy in the form of nutrients. Once the caterpillar has completed its growth phase, it enters the pupal stage, during which it undergoes metamorphosis to transform into an adult butterfly.
In summary, the larval stage of an insect's life cycle is a critical period of growth and development. It enables insects to accumulate energy, undergo moulting, and prepare for their transition into the next life stage. This stage's importance lies in its role as a preparatory phase for the insect's eventual transformation into its adult form.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.