
kinetic energy
Definition
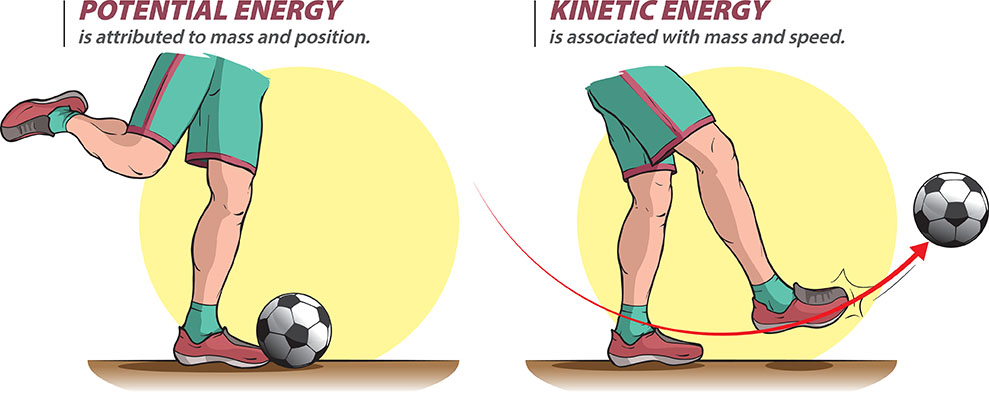
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. It is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. The kinetic energy of an object is directly proportional to its mass and its velocity squared.
The equation for kinetic energy is:
KE = 1/2mv²
where:
- KE is the kinetic energy
- m is the mass of the object
- v is the velocity of the object
Kinetic energy can be transferred from one object to another. For example, when a car hits a wall, the car's kinetic energy is transferred to the wall. This causes the wall to deform and the car to slow down.
Kinetic energy can also be converted into other forms of energy. For example, when a moving object is stopped, its kinetic energy is converted into heat energy. This is why brakes on cars get hot when they are used.
Kinetic energy is an important concept in physics. It is used to explain a wide range of phenomena, from the motion of objects to the transfer of heat.
How can the word be used?
The kinetic energy of the moving car was transferred to the wall when it crashed.
Different forms of the word
Noun: kinetic energy (plural: kinetic energies).
the energy of motion.
Adjective: kinetic.
relating to kinetic energy.
Verb: to kineticize.
to give kinetic energy to something.
Etymology
The word "kinetic" comes from the Greek word "κίνησις" (kinesis), which means "motion". The word "energy" comes from the Greek word "ἐνέργεια" (energeia), which means "activity" or "work".
So, kinetic energy is literally the energy of motion. It is the energy that is possessed by an object due to its motion. The greater the mass of an object and the faster it is moving, the more kinetic energy it has.
Question
What is kinetic energy?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the concept of kinetic energy and its significance in the study of physics. Provide examples of how kinetic energy is transformed and its relationship to an object's mass and velocity.
Answer:
Kinetic energy is a fundamental concept in physics that refers to the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It is an essential component of the study of energy and helps us understand the dynamic behaviour of objects.
The amount of kinetic energy an object possesses depends on both its mass and its velocity. The formula for calculating kinetic energy is KE = 0.5 * mass * velocity^2. This equation demonstrates that doubling an object's mass would result in double the kinetic energy while doubling its velocity would lead to a fourfold increase in kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is crucial because it exemplifies the relationship between motion and energy. When an object is in motion, it has the potential to do work or transfer energy to other objects upon collision. For example, a moving car possesses kinetic energy that can be converted into useful work, like stopping the car by applying brakes.
Additionally, kinetic energy is subject to the principle of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another. When a moving object comes to a halt, its kinetic energy transforms into other forms of energy, such as heat due to friction.
In essence, kinetic energy is a cornerstone concept in physics that underpins our understanding of motion, energy transformations, and the fundamental laws that govern the behaviour of objects in motion.