

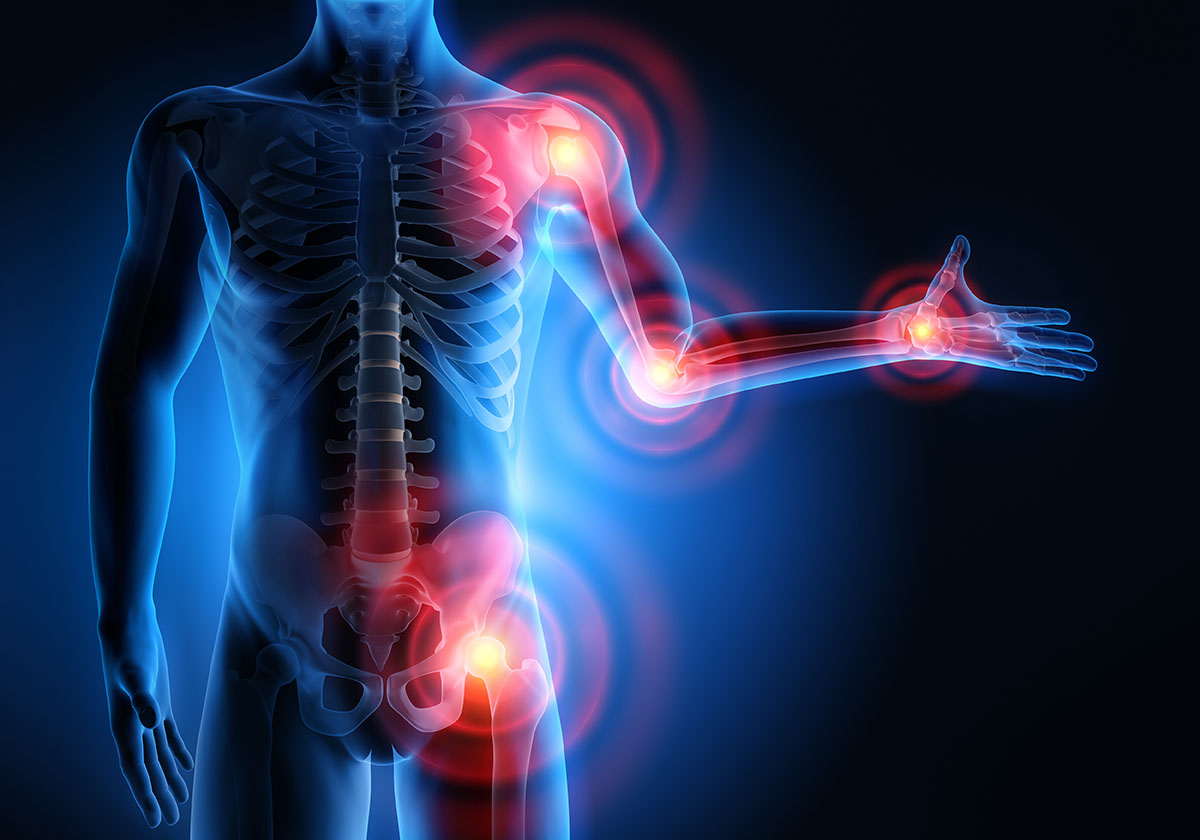
A joint is a structure that allows two or more bones to connect and move relative to each other. Joints are essential for movement, and they also help to support the body and protect the bones.
There are three main types of joints:
The different types of joints are held together by ligaments, which are tough bands of tissue. The ligaments help to keep the bones in place and prevent them from moving too much.
Joints are also lined with cartilage, which is a smooth, slippery tissue that helps to reduce friction between the bones. The cartilage also helps to absorb shock and protect the bones from injury.
Joints are important for our overall health and well-being. They allow us to move around, they support our body weight, and they protect our bones. It is important to take care of our joints by exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding injuries.
The surgeon called to say that I had a bad joint in my shoulder.
Noun:
Adjective:
Verb:
The word "joint" comes from the Old French word "joint", which means "to join". The Old French word "joint" is thought to be derived from the Latin word "jungere", which also means "to join".
What are joints?
Question:
Explain the structure and function of a joint in the human body. How do different types of joints enable various degrees of movement, and what role do ligaments play in joint stability?
Answer:
Joints are pivotal components of the human body's musculoskeletal system, facilitating movement and providing stability. They are formed where two or more bones meet, and their structure and function vary based on the type of joint.
There are three main types of joints: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. Synovial joints are the most common and allow the greatest range of movement. They consist of bones separated by a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid that lubricates the joint and reduces friction during movement.
Different types of synovial joints enable specific movements. Hinge joints, like the elbow, permit flexion and extension, while ball-and-socket joints, such as the hip, allow rotation, flexion, and extension. Ligaments, strong bands of connective tissue, play a critical role in joint stability by connecting bones and preventing excessive or abnormal movement.
Ligaments provide reinforcement to joints and limit their range of motion to prevent injury. However, they also enable controlled movement within the joint's natural range. Joint stability and movement are the result of a delicate balance between ligaments, muscles, and other connective tissues working together harmoniously.
Understanding joint structure and function is essential for comprehending human movement and the prevention of musculoskeletal injuries. The versatility and complexity of joints contribute to the incredible range of motion that the human body can achieve.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.