

The intestine is a long, muscular tube that is part of the digestive tract. It is where food is broken down and absorbed into the bloodstream.
The intestine is divided into three parts: the small intestine, the large intestine, and the rectum. The small intestine is where most of the digestion happens. The large intestine absorbs water and nutrients from the digested food. The rectum is where waste products are stored before they are eliminated from the body.
The intestine is lined with a layer of cells that secrete mucus. The mucus helps to protect the intestine from the acidic contents of the stomach. The intestine is also home to billions of bacteria. These bacteria help to break down food and produce vitamins.
The intestine is a very important organ. It helps us to get the nutrients we need to stay healthy. It also helps to protect us from disease.
The patient had a blockage in his intestines.
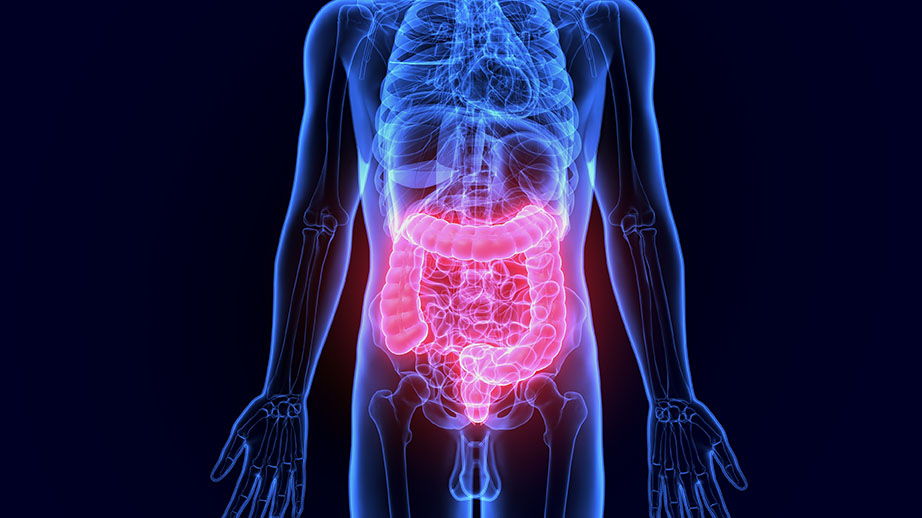
Noun: An intestine is a long, muscular tube that is part of the digestive system.
Adjective: Intestinal means relating to the intestines. For example, intestinal gas is gas that is produced in the intestines.
The word "intestine" comes from the Latin word "intestinum", which means "entrails" or "bowels". This is a very accurate description of the meaning of the word "intestine", as it refers to the long, muscular tubes that are part of the digestive system.
What do your intestines do?
Question:
Explain the role of the intestine in the digestive system, detailing its structure, functions, and the process of nutrient absorption. Discuss how the small and large intestines work together to break down and absorb food and highlight the importance of this process in providing energy and nutrients to the body.
Answer:
In conclusion, the intestine is a key player in the digestive system. Its structural adaptations and enzymatic actions in the small intestine, along with water absorption in the large intestine, enable the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients, ensuring the body's energy needs are met and essential substances are delivered to cells and tissues.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.