
incomplete circuit
Definition
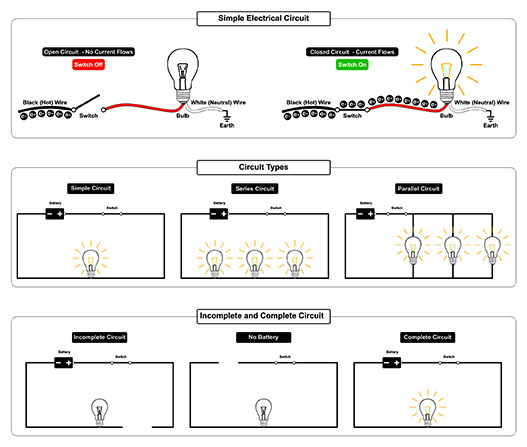
An incomplete circuit is a circuit that does not have a closed path for current to flow. This means that there is a break in the circuit somewhere, such as a switch that is turned off or a wire that is disconnected.
Incomplete circuits cannot produce electricity and do not work. This is because current cannot flow through a break in the circuit.
Incomplete circuits can be caused by a variety of things, such as:
- A broken wire
- A loose connection
- A switch that is turned off
- A component that is defective
Incomplete circuits can be dangerous. If you come across an incomplete circuit, it is important to turn off the power to the circuit before touching anything.
How can the word be used?
The electrician fixed the incomplete circuit in the wiring.
Different forms of the word
Noun: incomplete circuit.
Adjective: incomplete-circuit.
Etymology
The word "incomplete circuit" is a compound word made up of the words "incomplete" and "circuit".
The word "incomplete" comes from the Latin word "incompletus", which means "not complete". The word "circuit" comes from the Latin word "circum", which means "around".
So, the word "incomplete circuit" literally means "a circuit that is not complete". This is a very accurate description of what an incomplete circuit is.
Question
What is an incomplete circuit?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the concept of an incomplete circuit in electricity, detailing how it prevents the flow of electric current and the factors that can cause a circuit to become incomplete. Provide examples of everyday situations where an incomplete circuit occurs and its implications.
Answer:
An incomplete circuit refers to a pathway through which electric current cannot flow continuously due to a gap or interruption. It occurs when there is a break in the circuit, preventing the flow of electrons and interrupting the completion of the circuit loop.
Factors that can cause an incomplete circuit include the open position of a switch, a disconnected wire, or a damaged component. When the circuit is incomplete, electric current cannot flow from the source (such as a battery) to the destination (like a light bulb or motor), resulting in no functioning electrical device.
Everyday situations where an incomplete circuit occurs include turning off a light switch, unplugging an appliance, or a blown fuse in a household circuit. In a flashlight, for instance, pressing the switch closes the circuit, allowing current to flow and illuminating the bulb. Releasing the switch opens the circuit, causing the light to turn off.
Understanding incomplete circuits is crucial for electrical safety and troubleshooting. It helps prevent overloads and short circuits, minimising the risk of fires and electrical damage. By identifying and rectifying incomplete circuits, we ensure the proper functioning of electrical devices and maintain a safe environment in our homes and workplaces.