

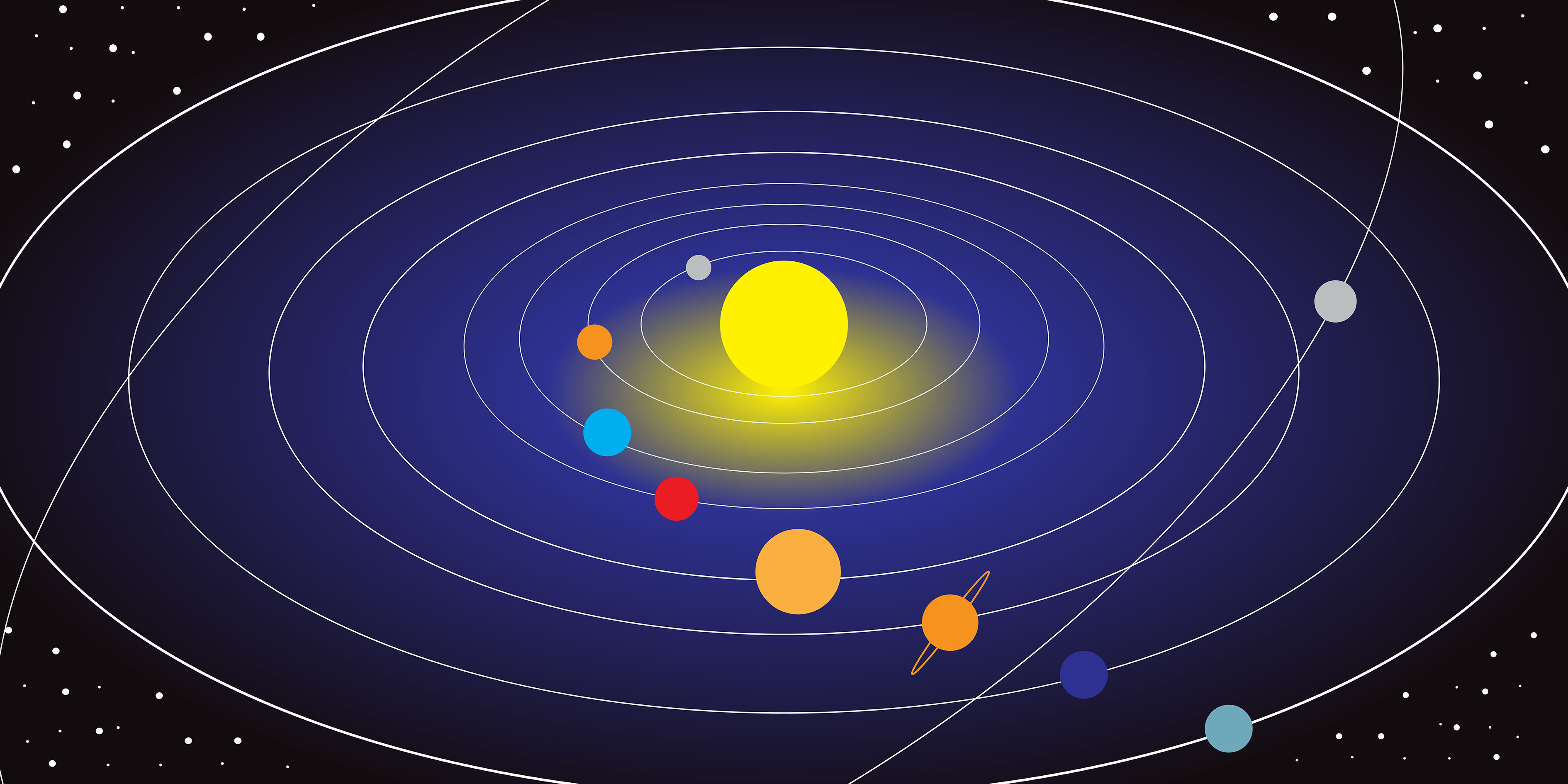
Heliocentric is an adjective that means "sun-centred." It is used to describe the model of the solar system in which the sun is at the centre and the planets revolve around it. This model was first proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century, and it superseded the previous model, which placed the Earth at the centre of the solar system.
The heliocentric model is supported by a number of observations, including the fact that the planets all revolve around the sun in the same direction and that they all have elliptical orbits. The heliocentric model also explains why we see different constellations in the sky at different times of the year.
The heliocentric model is a major breakthrough in astronomy, and it has had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe. It helped to replace the geocentric model, which was based on the belief that the Earth was the centre of the universe. The heliocentric model also helped to pave the way for the development of modern astronomy and astrophysics.
The heliocentric model is supported by a vast amount of evidence.
Noun: heliocentrism.
Adjective: heliocentric.
Adverb: heliocentrically.
The word "heliocentric" comes from the Greek words "helios", meaning "sun", and "kentron", meaning "center". It was first used in the 16th century to describe the model of the solar system in which the sun is at the centre.
What does heliocentric mean?
Question:
Explain the concept of a heliocentric solar system and discuss the key contributions of Nicolaus Copernicus in revolutionising our understanding of planetary motion.
Answer:
The heliocentric solar system is a model in which the Sun is at the centre, and the planets, including Earth, revolve around it in elliptical orbits. This model contrasts with the earlier geocentric view, where Earth was considered the centre of the universe.
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Renaissance mathematician and astronomer, played a pivotal role in transforming our understanding of celestial motion. In his seminal work "De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium" published in 1543, Copernicus presented a comprehensive heliocentric model, challenging the prevailing geocentric belief.
Copernicus proposed that Earth was not the centre of the universe and that the planets, including Earth, orbited the Sun. His model elegantly explained complex planetary motions, such as retrograde motion, which was challenging to account for in the geocentric system.
Although Copernicus' heliocentric model faced initial resistance, it laid the foundation for the scientific revolution and paved the way for future astronomers like Johannes Kepler and Galileo Galilei to refine and validate the heliocentric view. Copernicus' revolutionary insight marked a significant shift in our understanding of the cosmos, emphasising the importance of empirical observations and mathematical analysis in shaping our knowledge of the universe.