

Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and scientist who is considered the father of genetics. He conducted experiments on pea plants, and he discovered the basic principles of inheritance, which are still used today.
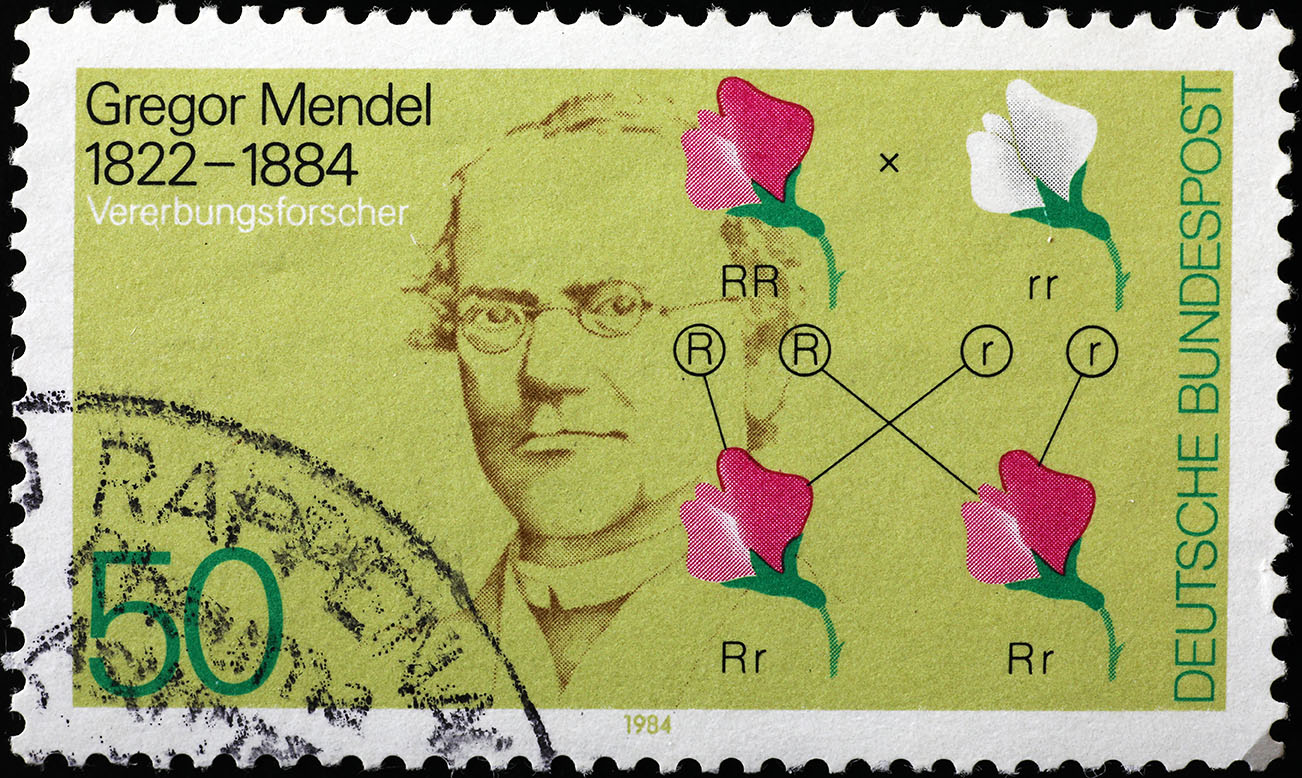
Mendel's experiments showed that traits are passed down in factors, which we now call genes. These genes come in pairs, and each parent passes one factor to each offspring. The different forms of a gene are called alleles. For example, the gene for flower colour has two alleles: one for purple flowers and one for white flowers.
Mendel's experiments also showed that the factors for different traits can segregate, or separate, during reproduction. This means that offspring do not always have the same traits as their parents. For example, if a parent has purple flowers and the other parent has white flowers, the offspring will have either purple flowers or white flowers, but not both.
Mendel's work laid the foundation for the science of genetics, and his discoveries are still used today to understand how traits are passed down from generation to generation.
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and botanist who is considered the father of genetics.
There are no different forms of the word "Gregor Mendel" because it is a proper noun. Proper nouns are the names of specific people, places, or things. They are always capitalized, even in the middle of a sentence.
The name "Gregor Mendel" is of German origin. The first element, "Gregor", is a common German given name that means "watchful" or "alert". The second element, "Mendel", is a habitational name from any of the places called Mendel, which are derived from the Old German word "mendel", which means "boundary" or "border".
What is Gregor Mendel famous for?
Question:
What did Gregor Mendel do for science?
Answer:
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and botanist who is considered the father of genetics. He conducted experiments on pea plants that helped him to formulate the laws of inheritance, which are the basic principles of genetics.
Mendel's experiments showed that traits are passed down from parents to offspring in predictable patterns. He also showed that there are two factors for each trait, one from each parent, and that these factors can be dominant or recessive. Mendel's work laid the foundation for the modern understanding of genetics and has had a profound impact on biology and medicine.
Here are some additional points that could be included in the answer:
Mendel's laws of inheritance are:
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.