
greenhouse gases
Definition
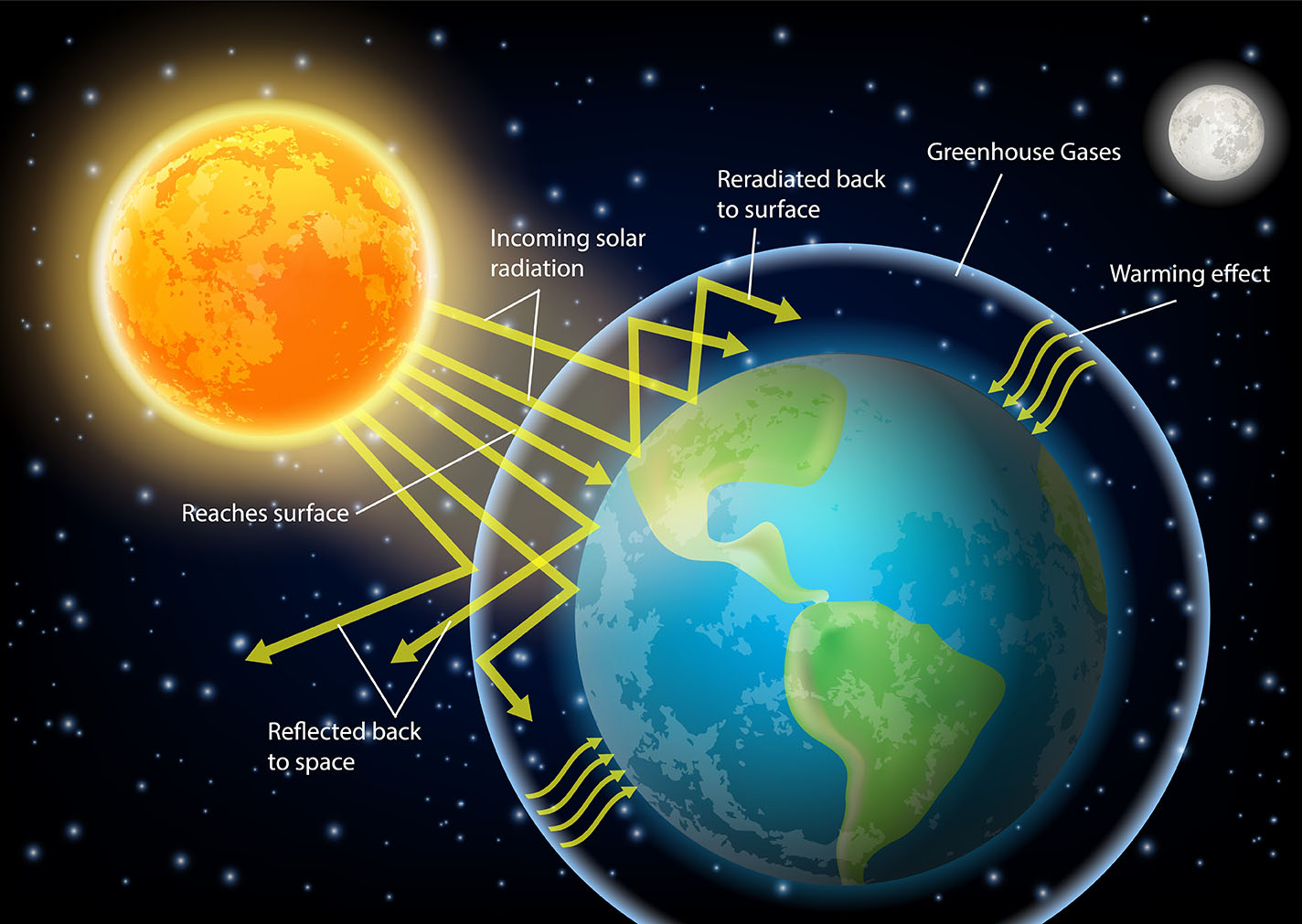
Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat from the sun. This heat keeps Earth's temperature warm enough to support life. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
Greenhouse gases work like a blanket around Earth. They allow sunlight to pass through the atmosphere, but they trap the heat that is reflected back from Earth's surface. This heat keeps Earth warm.
The amount of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere has been increasing over time. This is due to human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. The increase in greenhouse gases is causing Earth to warm up, which is leading to climate change.
Climate change is a serious threat to the planet. It is causing the sea level to rise, extreme weather events to become more common, and glaciers to melt. We need to reduce our emissions of greenhouse gases in order to prevent the worst effects of climate change.
How can the word be used?
The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of greenhouse gases.
Different forms of the word
Noun: greenhouse gas.
Adjective: greenhouse gas.
Verb: to greenhouse gas.
Synonym: heat-trapping gas.
Etymology
The term "greenhouse gases" was first used in the early 1900s to describe gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, like the glass in a greenhouse. The term is derived from the Old English words "grene" (green) and "hus" (house).
Question
What are greenhouse gases?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
What are greenhouse gasses and how do they affect the climate?
Answer:
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that trap heat from the sun. This heat helps to keep the Earth warm and habitable. However, human activities are releasing greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere at an increasing rate, which is causing the greenhouse effect to become stronger. This is leading to global warming, which is a major threat to the planet.
The main greenhouse gasses are:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Methane (CH4).
- Nitrous oxide (N2O).
- Ozone (O3).
- Water vapour (H2O).
These gases trap heat in the atmosphere by absorbing infrared radiation. Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by the sun and by the Earth's surface. When greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation, they heat up. This heat is then released back into the atmosphere, which keeps the Earth warm.
Human activities are releasing greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere at an increasing rate. This is due to the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, release carbon dioxide when they are burned. Deforestation removes trees, which absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Agriculture releases methane and nitrous oxide from livestock and fertilisers.
The increasing levels of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere are causing the greenhouse effect to become stronger. This is leading to global warming, which is a major threat to the planet. Global warming is causing the Earth's temperature to rise, which is leading to a number of problems, including:
- Rising sea levels.
- Melting glaciers.
- More extreme weather events.
- Changes in plant and animal life.
It is important to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of global warming. This can be done by using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing deforestation.