

Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of two solid surfaces in contact. It is caused by the interaction of the surface asperities. Asperities are tiny bumps and ridges on the surface of a material. When two surfaces come into contact, the asperities on one surface interlock with the asperities on the other surface, creating friction.
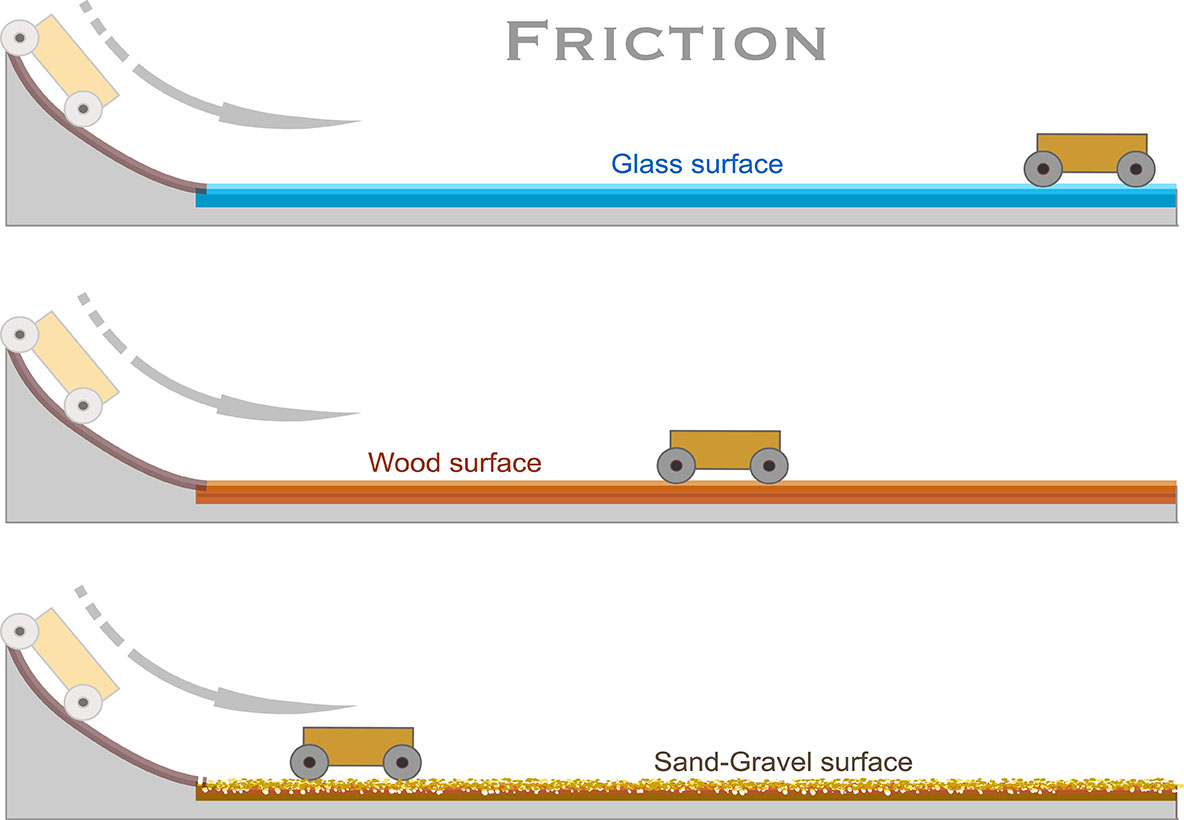
The amount of friction between two surfaces depends on the following factors:
Friction can be a useful force. For example, it helps us to walk and drive cars. However, it can also be a harmful force. For example, it can cause wear and tear on machines and it can make it difficult to move heavy objects.
The friction of the water against the boat's hull slowed it down.
Noun: friction, frictions.
Adjective: frictional.
The word "friction" comes from the Latin word frictio, which means "rubbing" or "friction". The Latin word frictio is made up of the verb fricare, which means "to rub", and the suffix -tio, which indicates an action.
Which of the following surfaces would provide the greatest amount of friction and why? Sand, Carpet, Wood, Tile.
Question:
Explain the concept of friction and its role in everyday life and various physical processes. Describe the factors that influence friction, including surface roughness, applied force, and the type of materials in contact. Provide real-life examples of how friction affects motion, such as walking, driving, and slowing down moving objects. Discuss the significance of reducing friction in certain situations and the practical applications of friction in engineering and technology.
Answer:
Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion or attempts of motion between two surfaces in contact. It plays a crucial role in everyday life and various physical processes. The roughness of the surfaces, the applied force, and the type of materials influence the amount of friction present.
Real-life examples of friction's impact on motion include the ability to walk without slipping, the traction between car tires and the road, and the braking system that slows down moving vehicles.
In certain situations, reducing friction is desirable, such as using lubricants to minimise wear and tear in machinery. On the other hand, friction finds practical applications in engineering, where it helps in designing effective brakes, tires, and clutches. Understanding and managing friction is essential in optimising performance and safety in various technological applications.