

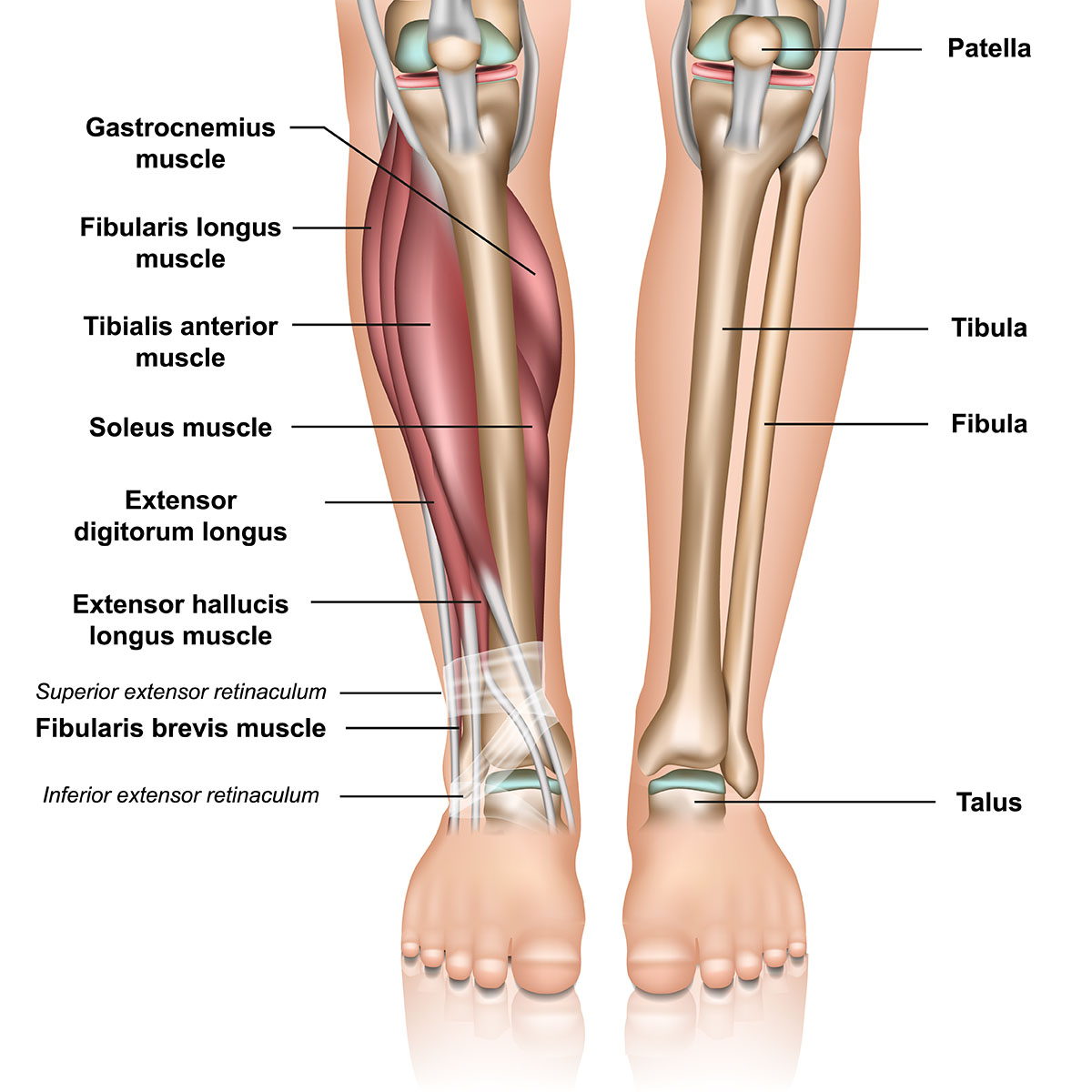
The fibula is the smaller of the two bones in the lower leg. It is located on the outside of the leg, and it runs from the knee to the ankle. The fibula is not as strong as the tibia, the larger bone in the lower leg. However, it is important for stability and helps to prevent the tibia from twisting.
The fibula is also important for movement. It helps to move the ankle by rotating around the tibia. The fibula also helps to stabilise the ankle joint by providing a surface for the ligaments to attach to.
The fibula is also a site for muscle attachment. Several muscles attach to the fibula, including the peroneal muscles, which help to move the foot.
The doctor diagnosed the patient with a broken fibula.
Noun: fibula, fibulae.
Adjective: fibular.
The word "fibula" is derived from the Latin word fībula, which means "pin" or "clasp". The Latin word fībula is thought to be derived from the Proto-Indo-European root *dheigw-, which also means "to stick, fix".
Where is your fibula located?
Question:
Explain the role of the fibula in the human skeletal system and its interaction with other bones. Describe the main functions of the fibula and how it contributes to stability and movement in the lower limb. Provide real-life examples of injuries or conditions related to the fibula.
Answer:
The fibula is one of the two long bones in the lower leg, located on the lateral side (outer side) of the tibia. It plays a crucial role in the human skeletal system, providing support and stability to the lower limb. While the tibia bears most of the body's weight, the fibula assists in weight-bearing and functions as a point of attachment for various muscles involved in ankle and foot movement.
The fibula's structural support and connection with the tibia help to distribute forces during weight-bearing activities like walking, running, and jumping. Additionally, the fibula contributes to joint stability and assists in maintaining balance.
Real-life examples of fibula-related injuries include fractures, commonly caused by sports-related accidents or falls. Additionally, conditions like fibular stress fractures, where repetitive stress leads to tiny cracks in the bone, can occur in athletes engaging in high-impact activities.
In conclusion, the fibula is an essential bone in the lower limb, contributing to stability, movement, and weight-bearing functions. Understanding its role in the skeletal system aids in comprehending the mechanics of lower limb motion and assists in diagnosing and treating related injuries or conditions.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.