

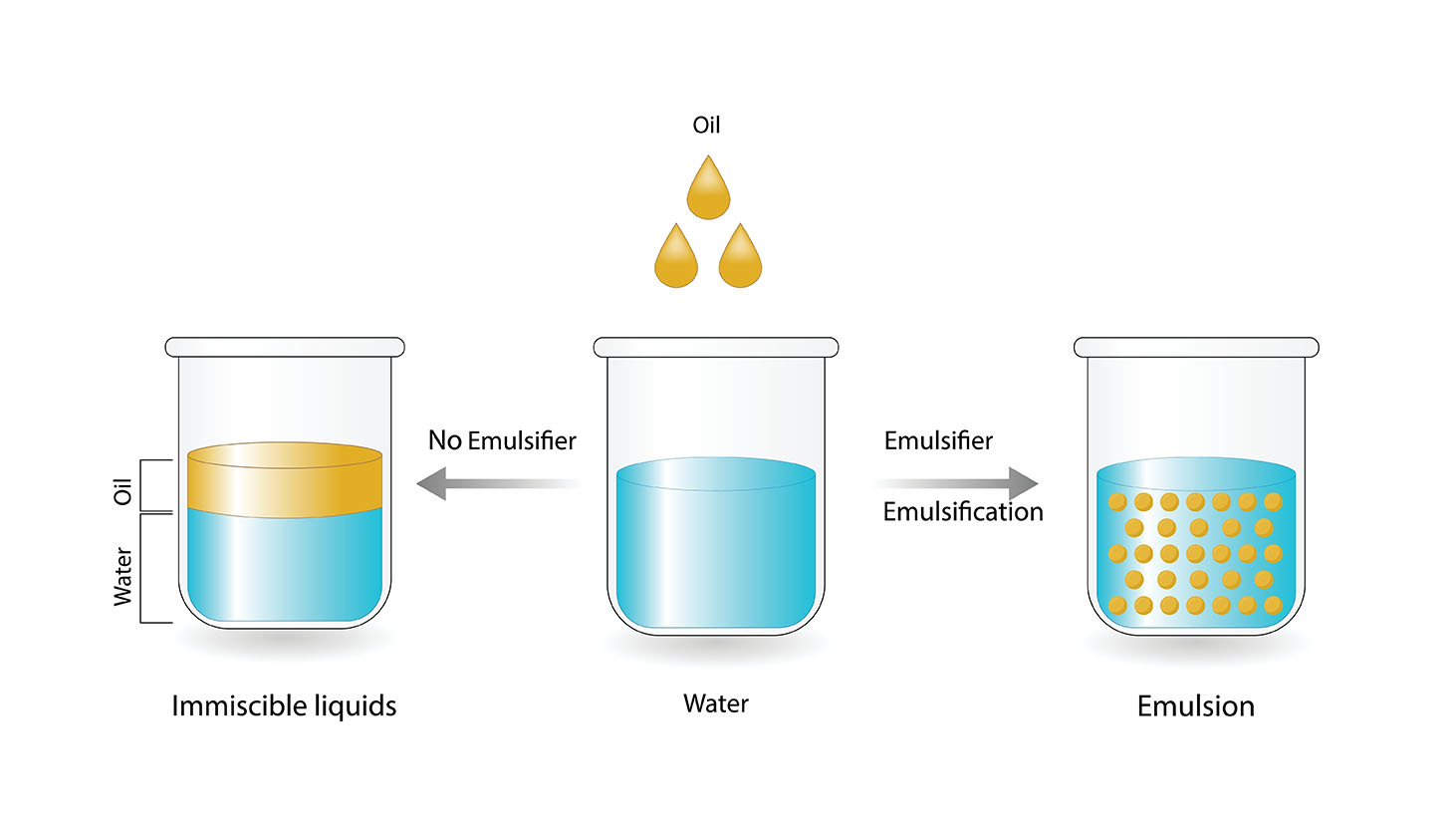
To emulsify means to mix two liquids that normally do not mix together, such as oil and water. This is done by adding an emulsifier, which is a substance that helps to keep the two liquids from separating.
Emulsifiers work by forming a film around the droplets of one liquid, which prevents them from coming into contact with the other liquid. This allows the two liquids to stay mixed together even though they are not miscible.
There are many different types of emulsifiers, including soaps, detergents, and proteins. The type of emulsifier that is used depends on the specific application. For example, soaps are often used to emulsify oil and water in food products, while detergents are often used to emulsify oil and water in cleaning products.
Emulsions are used in many different products, including mayonnaise, salad dressing, sunscreen, and paints. They are also used in the food industry to make products that are more stable and have a longer shelf life.
An emulsion is a stable mixture of two liquids that would normally not mix together.
Noun: emulsion, emulsification.
Adjective: emulsive.
Verb: to emulsify.
Synonyms: blend, mix, combine.
Antonyms: separate, divide, segregate.
The word "emulsify" comes from the Latin word emulgere, which means "to milk out". The word emulgere is made up of two Latin words: e (out) and mulgere (to milk).
What does emulsify mean?
Question:
Explain the process of emulsification and its significance in food preparation and digestion. Describe how emulsifiers facilitate the mixing of immiscible substances, such as oil and water, and the formation of stable emulsions. Provide examples of emulsification in everyday foods, such as mayonnaise and salad dressings, and its role in enhancing flavour and texture.
Answer:
Emulsification is a process that involves the mixing of two immiscible substances, such as oil and water, to form a stable emulsion. Emulsifiers are substances that facilitate this process by stabilising the interface between the oil and water droplets. They have hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions that allow them to interact with both substances, preventing them from separating.
In food preparation, emulsification is vital in creating products like mayonnaise and salad dressings. Mayonnaise, for example, contains oil and vinegar, which are typically immiscible. Emulsifiers like lecithin in egg yolks stabilise the mixture, giving mayonnaise its creamy texture and preventing oil and vinegar from separating.
In digestion, bile salts in the small intestine emulsify dietary fats, breaking them into smaller droplets for efficient digestion and absorption. Emulsification enhances the flavour and texture of various foods, making them more palatable and enjoyable.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.