
electron
Definition
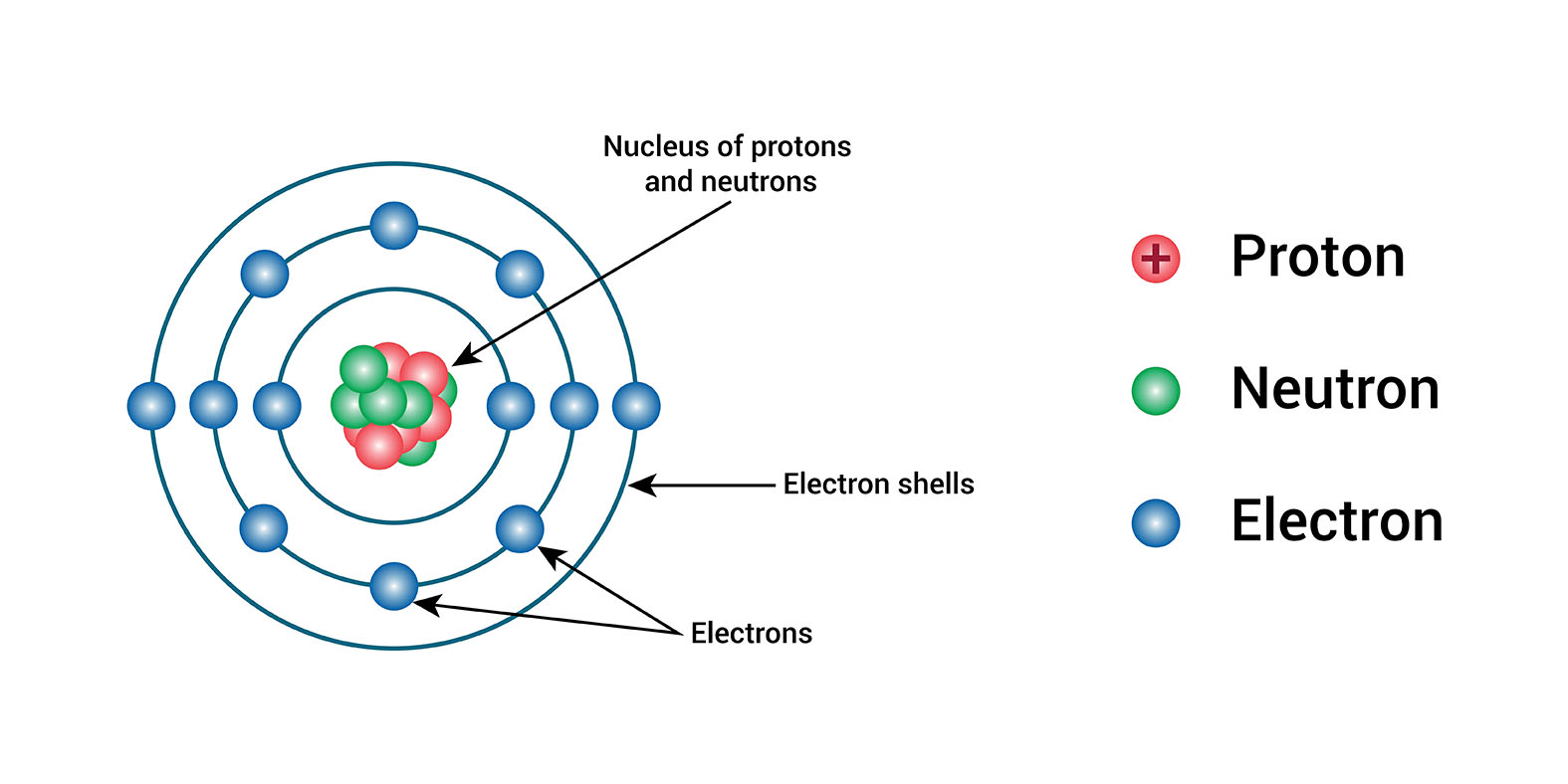
An electron is a subatomic particle that has a negative electrical charge. It is one of the three fundamental particles of matter, along with protons and neutrons. Electrons are found in all atoms, and they orbit the nucleus of the atom.
The mass of an electron is very small, about 1/1836 the mass of a proton. Electrons have a charge of -1, which means that they have one more negative charge than a proton. The charge of an electron is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton.
Electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom in shells. The first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight electrons, and so on. The number of electrons in an atom's shells determines the chemical properties of the atom.
The energy levels of electrons are quantized, which means that they can only have certain values. This is why electrons can only orbit the nucleus in certain shells.
Electrons can also be found in free-electron states, which means that they are not bound to any atom. Free-electron states can be found in metals, where the electrons are free to move around.
Electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of atoms because they can be transferred from one atom to another. When electrons are transferred, they create ions. An ion is an atom that has lost or gained electrons. Positive ions have lost electrons, and negative ions have gained electrons.
The transfer of electrons is what allows chemical reactions to happen. Chemical reactions are the basis of all life on Earth, so electrons play a vital role in our existence.
How can the word be used?
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge.
Different forms of the word
Noun: electron.
Adjective: electronic.
Verb: to electronify, electrize.
Synonym: charge, particle, unit.
Antonym: uncharged, neutral.
Etymology
The word "electron" comes from the Greek word elektron, which means "amber". Amber is a fossilized tree resin that can be rubbed to produce a static electric charge.
Question
What are electrons responsible for?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the fundamental properties and significance of electrons in the atomic structure. Describe the role of electrons in chemical bonding and the formation of compounds. Provide examples of everyday applications of electron behaviour, such as electricity conduction in metals and semiconductors.
Answer:
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit around the nucleus of an atom. They play a vital role in determining an element's chemical properties and behaviour. The arrangement of electrons in electron shells defines an atom's chemical reactivity and bonding capabilities.
In chemical bonding, electrons are either shared or transferred between atoms, leading to the formation of compounds. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons. These interactions create the vast array of molecules and materials that make up our world.
The behaviour of electrons is also central to electricity conduction in materials like metals and semiconductors. In metals, electrons are free to move, facilitating electrical current flow. Semiconductors' unique electron behaviour allows them to be used in electronics and computers.
Understanding electron properties is essential in various scientific fields, from chemistry and materials science to electronics and nanotechnology, driving innovation and technological advancements that impact our daily lives.