
ear
Definition
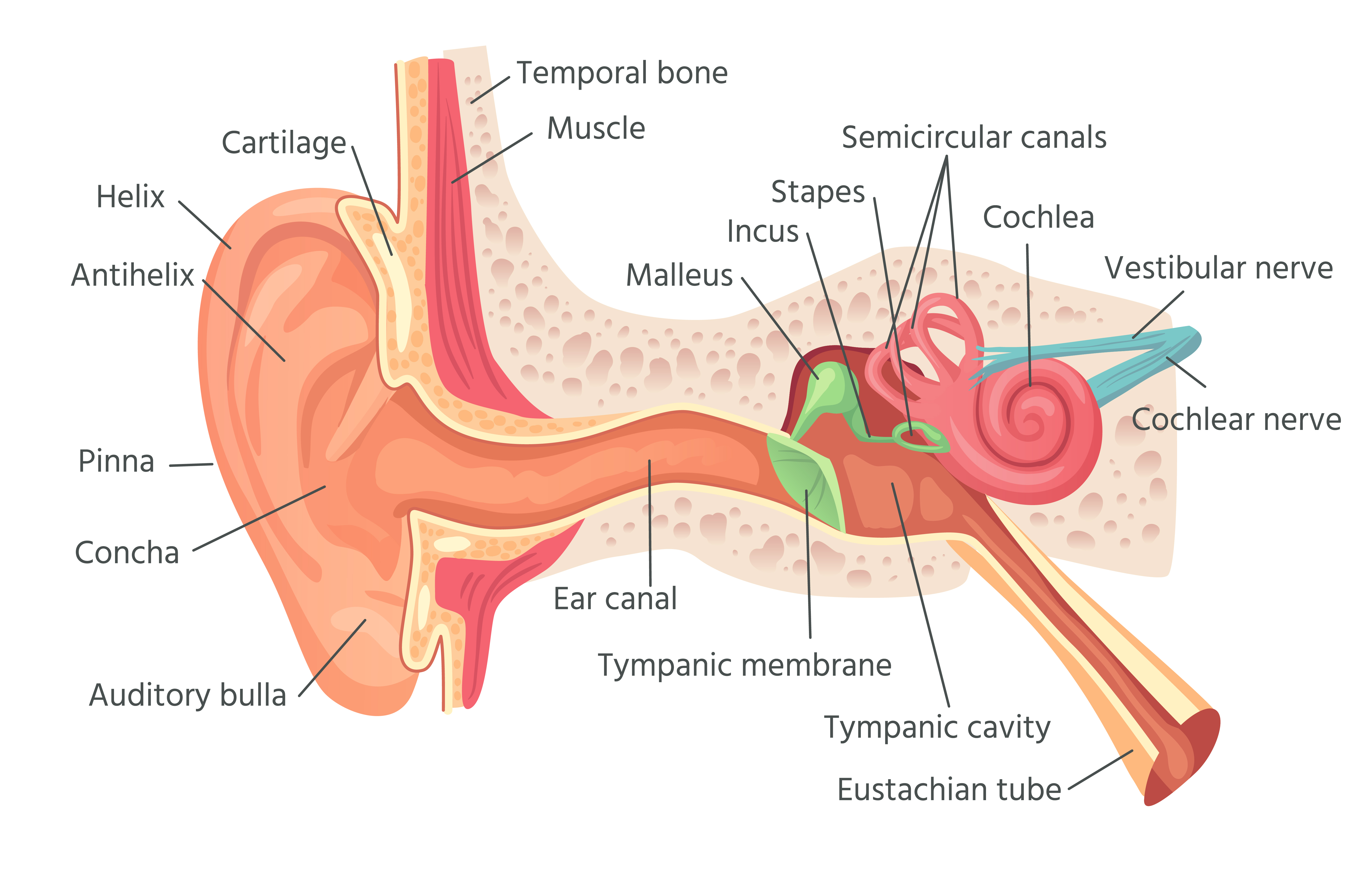
An ear is a sense organ that allows us to hear. It is located on the side of the head, and it is made up of three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
The outer ear is the part of the ear that we can see. It is made up of the pinna, the ear canal, and the eardrum. The pinna helps to collect sound waves, and the ear canal directs the sound waves to the eardrum. The eardrum vibrates when it receives sound waves, and these vibrations are then transmitted to the middle ear.
The middle ear is a small, air-filled cavity that contains three bones: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. These bones amplify the vibrations from the eardrum and transmit them to the inner ear.
The inner ear is a complex structure that contains the cochlea, the organ of hearing. The cochlea is a spiral-shaped chamber that is filled with fluid. When the vibrations from the middle ear reach the cochlea, they cause the fluid to move. This movement stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea, which send signals to the brain. The brain interprets these signals as sound.
There are three types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem with the outer ear or the middle ear. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is a problem with the inner ear or the auditory nerve. Mixed hearing loss is a combination of conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
How can the word be used?
The cat's ears perked up when she heard the sound of the doorbell.
Different forms of the word
Noun: ear, auricle, auditory organ, pinna.
Verb: to ear, to hear.
Adjective: aural, auricular, auditory.
Synonym: auditory canal, auditory nerve.
Antonym: eye.
Etymology
The word "ear" comes from the Old English word "ēare", which means "ear". It is made up of the two Old English words "ēa" (ear) and "r" (to grow).
Question
Why do you think you have two ears?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the structure and functions of the human ear. Describe the process of hearing, including how sound waves are detected and transmitted through the ear to the brain. Provide examples of how the ear's intricate mechanism allows us to perceive different frequencies and intensities of sound.
Answer:
The human ear is a complex sensory organ responsible for hearing and maintaining balance. It consists of three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and funnels them through the ear canal to the eardrum in the middle ear. The eardrum vibrates in response to the sound waves, and these vibrations are amplified by three tiny bones (ossicles) called the hammer, anvil, and stirrup.
The vibrations are then transmitted to the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear, where hair cells convert them into electrical signals. These signals are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound.
The ear's intricate mechanism allows us to perceive different frequencies as pitch and varying sound wave amplitudes as loudness. For instance, high-frequency sounds, like bird songs, activate specific regions of the cochlea, while low-frequency sounds, such as bass music, stimulate different areas.
Understanding the structure and functions of the ear helps us appreciate the remarkable auditory capabilities that enable us to experience and interpret the rich tapestry of sounds in our environment.