
dwarf planet
Definition
A dwarf planet is a celestial body that meets the following three criteria:
- 1. It is in orbit around the Sun.
- 2. It has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape.
- 3. It has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.
Dwarf planets are not considered planets because they do not meet the third criterion. Planets have cleared the neighbourhood around their orbit, meaning that they are the dominant gravitational bodies in their orbit. Dwarf planets, on the other hand, share their orbit with other objects, such as asteroids or comets.
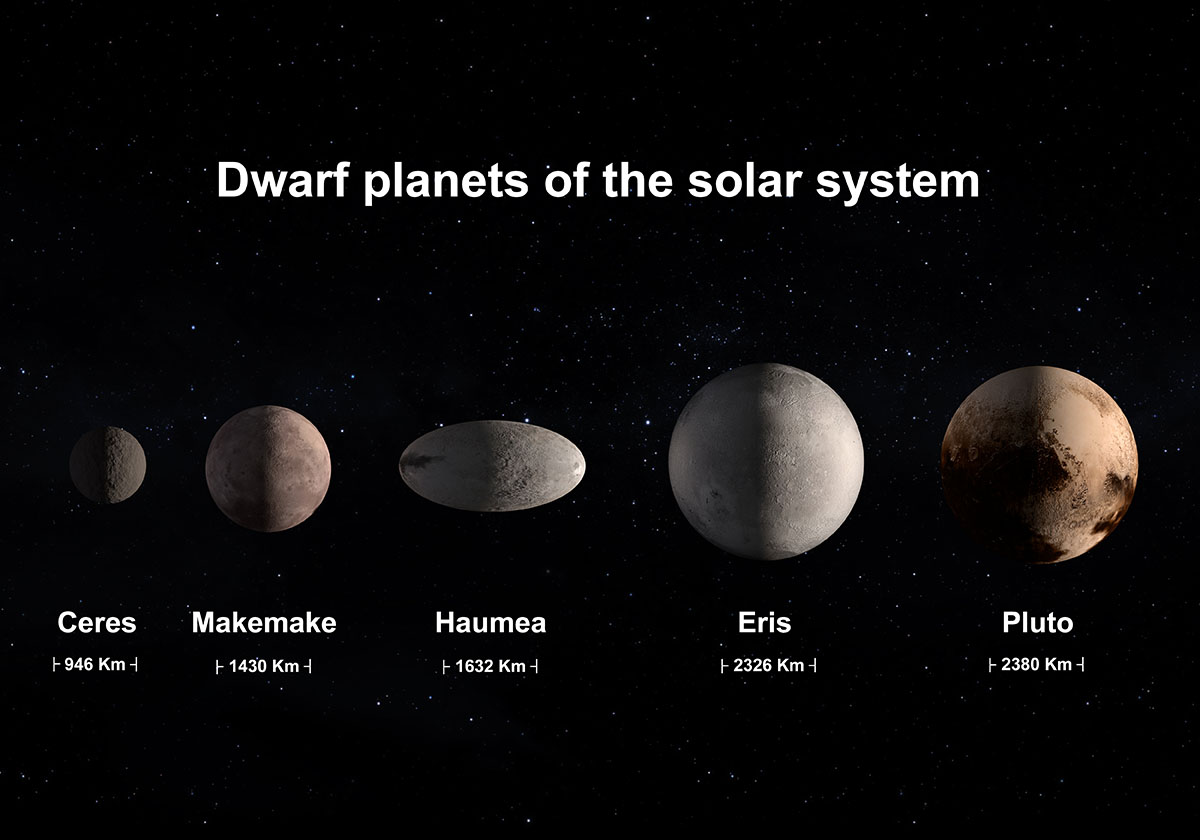
There are five known dwarf planets in the Solar System: Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake. Ceres is the largest dwarf planet, and it is located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Pluto is the most famous dwarf planet, and it was originally classified as a planet until 2006. Eris is the second-largest dwarf planet, and it is located in the Kuiper belt beyond Neptune. Haumea and Makemake are smaller dwarf planets, and they are also located in the Kuiper belt.
Dwarf planets are an important part of the Solar System, and they play a role in understanding the formation and evolution of our solar system.
How can the word be used?
One of the five dwarf planets in the Solar System: Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake.
Different forms of the word
Noun: dwarf planet.
Adjective: dwarf planetary.
Verb: to dwarf planet.
Synonym: minor planet, small solar system body.
Antonym: planet.
Etymology
The word "durable" comes from the Latin word dūrāre, which means "to last." It is made up of the two Latin words dūrus (hard) and āre (to make).
Question
What is the difference between a planet and a dwarf planet?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
Explain the characteristics and classification of a dwarf planet in our solar system. Describe the key criteria established by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for a celestial body to be designated as a dwarf planet. Provide examples of known dwarf planets in our solar system and discuss their significance in our understanding of planetary bodies.
Answer:
A dwarf planet is a celestial body that shares some characteristics with planets but does not meet all the criteria to be classified as a full-fledged planet. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has set three key criteria for an object to be designated as a dwarf planet: it must orbit the Sun, have enough mass for self-gravity to form a nearly round shape, and must not have cleared its orbital path of other debris.
Examples of dwarf planets in our solar system include Pluto, Eris, and Ceres. Pluto, once considered the ninth planet, was reclassified as a dwarf planet due to its small size and irregular orbit. Eris and Ceres are also notable dwarf planets.
Studying dwarf planets is significant as it helps us understand the diversity of celestial bodies in our solar system and the processes that shaped them. They provide insights into the early solar system's formation and offer valuable information about planetary evolution and dynamics.