

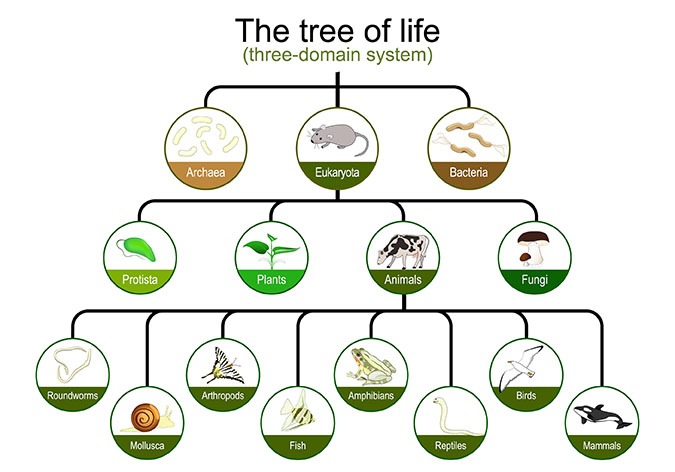
A domain is a taxonomic category that is used to classify living things. It is the highest level of classification, above kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
The three domains of life are Eukarya, Bacteria, and Archaea.
The dominant species in the forest is the oak tree.
Noun: domain.
Adjective: dominant.
Verb: dominate.
Adverb: dominantly.
Synonym: sphere, territory, field.
Antonym: subservience.
The word "domain" comes from the Latin word dominium, which means "ownership" or "lordship". It is made up of the two Latin words domus (house) and -inium (suffix denoting possession).
What does the word domain mean?
Question:
Explain the concept of a domain in the context of biology and its significance in classifying and understanding life's diversity. Describe the three main domains of life and provide examples of organisms found in each domain.
Answer:
In biology, a domain is the highest taxonomic rank used to classify and categorize all living organisms. It represents a broad level of classification that groups organisms based on fundamental differences in their cellular structure, biochemical processes, and evolutionary history. The three main domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Understanding the three domains of life provides a fundamental framework for studying life's diversity and evolutionary relationships among different organisms. It helps scientists organize and comprehend the complexity of life on Earth.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.