

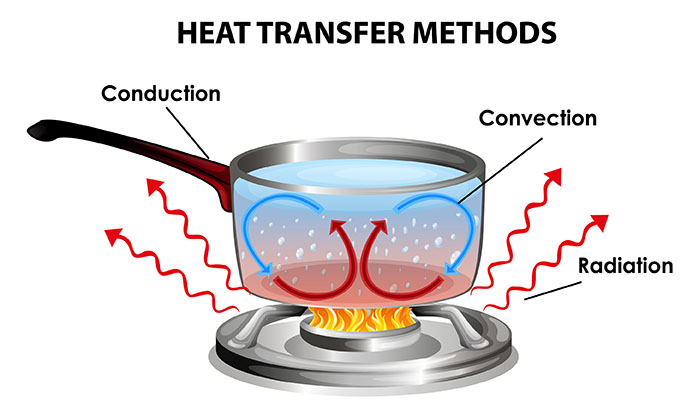
Conduction is the transfer of heat energy through a solid, liquid, or gas by direct contact.
This happens when the molecules in the material vibrate and collide with each other.
The heat energy is transferred from the molecules that are vibrating more to the molecules that are vibrating less.
The rate of conduction depends on the material, the temperature difference, and the surface area.
The electrical current was conducted through the copper wire.
Noun:
Conduction: The transfer of heat or electricity through a material by means of collisions between the particles of the material.
Adjective:
Conductive: Able to conduct heat or electricity.
Verb:
To conduct: To transfer heat or electricity through a material by means of collisions between the particles of the material.
The word "conduction" comes from the Latin word "conductus", which means "to lead". It is made up of the prefix "con-", which means "together", and the verb "ducere", which means "to lead".
Explain how conduction works.
Question:
Define conduction in the context of heat transfer and provide an example to illustrate how it occurs.
Answer:
Conduction is a process of heat transfer in which heat energy is transferred through a material by direct molecular interaction. In this process, heat flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature within the material, leading to an equalisation of temperatures over time.
An example of conduction is when you place a metal spoon in a cup of hot coffee. The heat from the hot coffee is conducted through the metal spoon's molecules, causing the spoon's handle to become warm. As a result of conduction, the heat is distributed evenly from the hot coffee to the entire metal spoon, making it possible for the handle to be warm to the touch.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.