
closed electric circuit
Definition
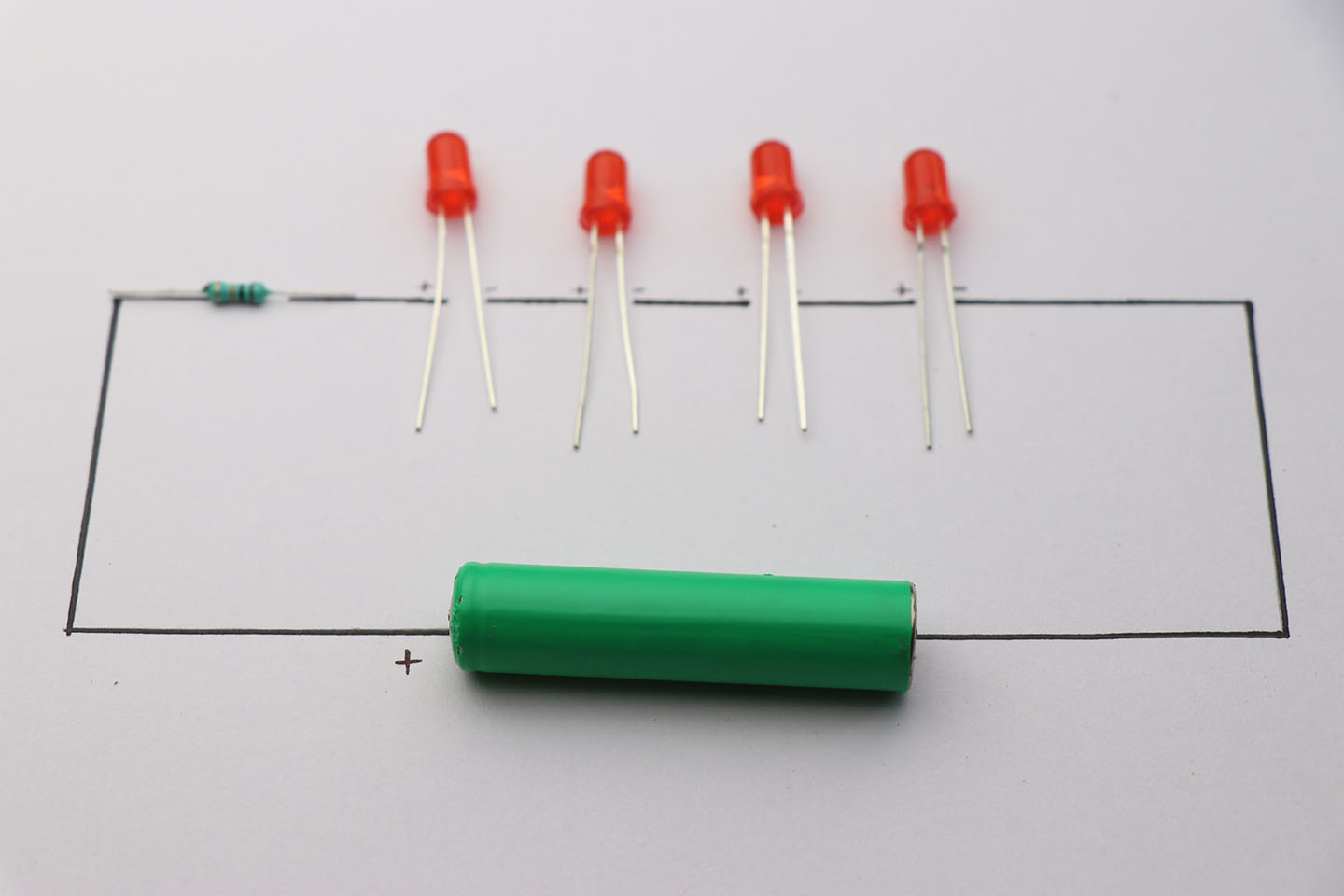
A closed electric circuit is a pathway that electricity can flow through without interruption. This means that the circuit must be complete, with no breaks in the wire or other components.
The current in a closed circuit is created by the flow of electrons, which are negatively charged particles.
The electrons flow from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal, and they do work as they flow through the circuit.
The amount of work that the electrons can do depends on the strength of the current and the resistance of the circuit.
How can the word be used?
The fuse blew, breaking the closed electric circuit.
Different forms of the word
Noun:
Singular: closed electric circuit.
Plural: closed electric circuits.
Adjective:
Closed-circuit: relating to a closed electric circuit.
Etymology
The word "closed electric circuit" is made up of three words: "closed", "electric", and "circuit".
Closed: This word comes from the Latin word "clausus", which means "shut" or "closed".
Electric: This word comes from the Greek word "elektron", which means "amber".
Circuit: This word comes from the Latin word "circuitus", which means "a going around".
Question
What is the difference between a closed electric circuit and an open electric circuit?
AQA Science Exam Question and Answer
Question:
What is a closed electric circuit, and how does it function in the context of electric current flow?
Answer:
A closed electric circuit is a complete loop or pathway that allows electric current to flow from the source, through various components like resistors or light bulbs, and back to the source. In a closed circuit, there are no interruptions or gaps, ensuring a continuous flow of electric charge. This flow of electrons allows electrical devices to operate, as the current can transfer energy and perform useful work within the circuit. Without a closed circuit, the flow of electrons would be disrupted, resulting in the interruption of electrical devices and preventing them from functioning properly.