

Chronic means long-lasting or persistent. A chronic condition is one that lasts for a long time, usually more than three months. Chronic conditions can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Some common chronic conditions include:
Chronic conditions can have a significant impact on a person's life. They can cause pain, fatigue, and disability. They can also make it difficult to work, go to school, and participate in activities.
There is no cure for most chronic conditions, but they can be managed with treatment. Treatment may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
It is important to manage chronic conditions well because they can lead to serious complications, such as heart attack, stroke, and death.
Here are some of the key things to know about chronic conditions:
The patient has a chronic illness.
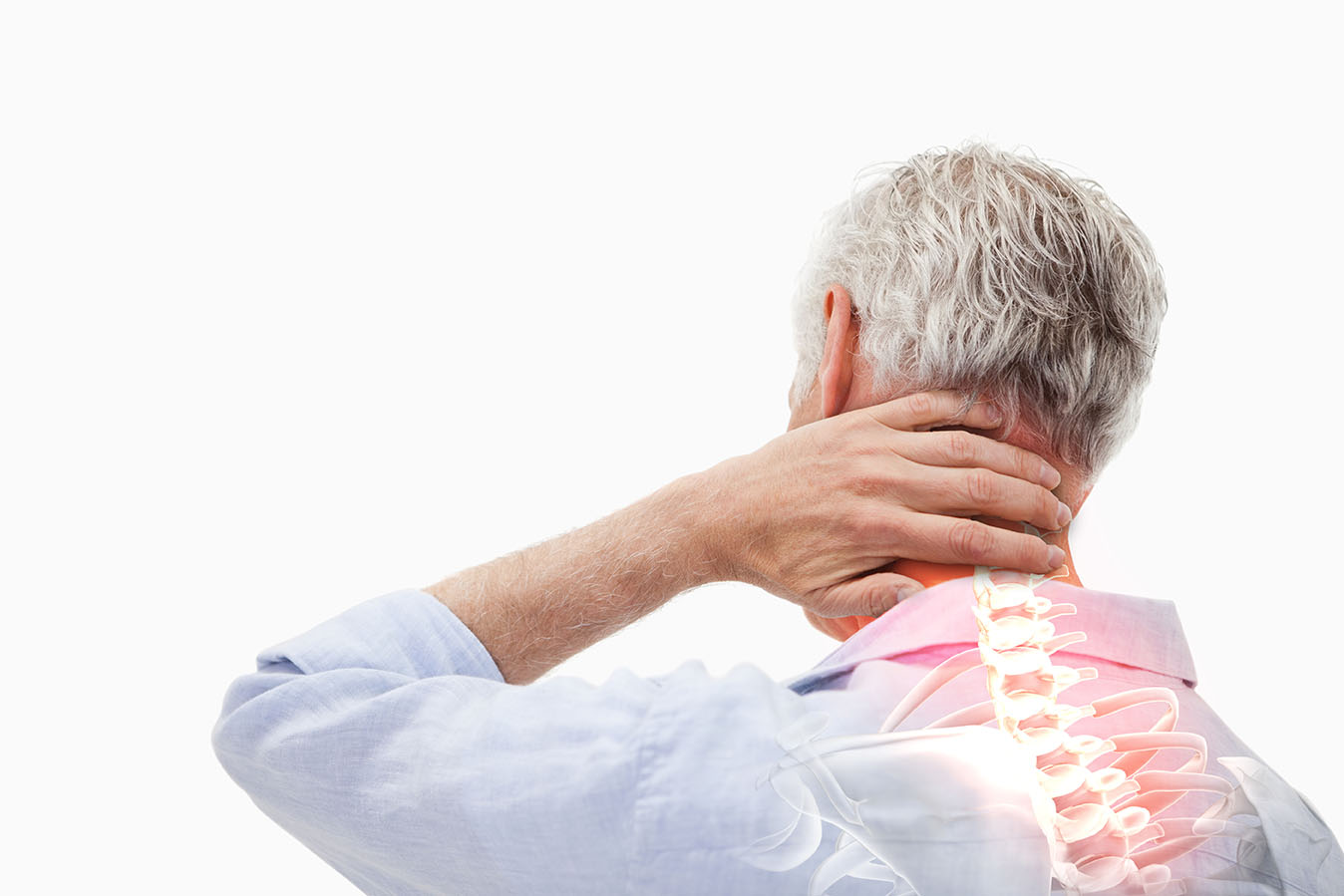
Noun: chronic (plural: chronics).
Adjective: chronic.
Adverb: chronically.
Verb: to chronicle.
The word "chronic" comes from the Greek word "khronikos", which means "of long duration". The word "chronic" was first used in English in the 16th century to refer to a disease that is long-lasting or persistent.
Identify some examples of chronic pain.
Question:
What is the difference between acute and chronic diseases?
Answer:
Acute diseases are short-term illnesses that usually resolve on their own within a few weeks or months. Chronic diseases are long-term illnesses that can last for years or even decades.
Some examples of acute diseases include the common cold, the flu, and strep throat. Some examples of chronic diseases include diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Acute diseases are usually caused by a specific event, such as a virus or bacteria. Chronic diseases are often caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
Acute diseases are usually treated with medication or other therapies. Chronic diseases are often managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.