

Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17.
It is a pale yellow-green gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Chlorine is a highly reactive element and is used in a variety of applications, including:
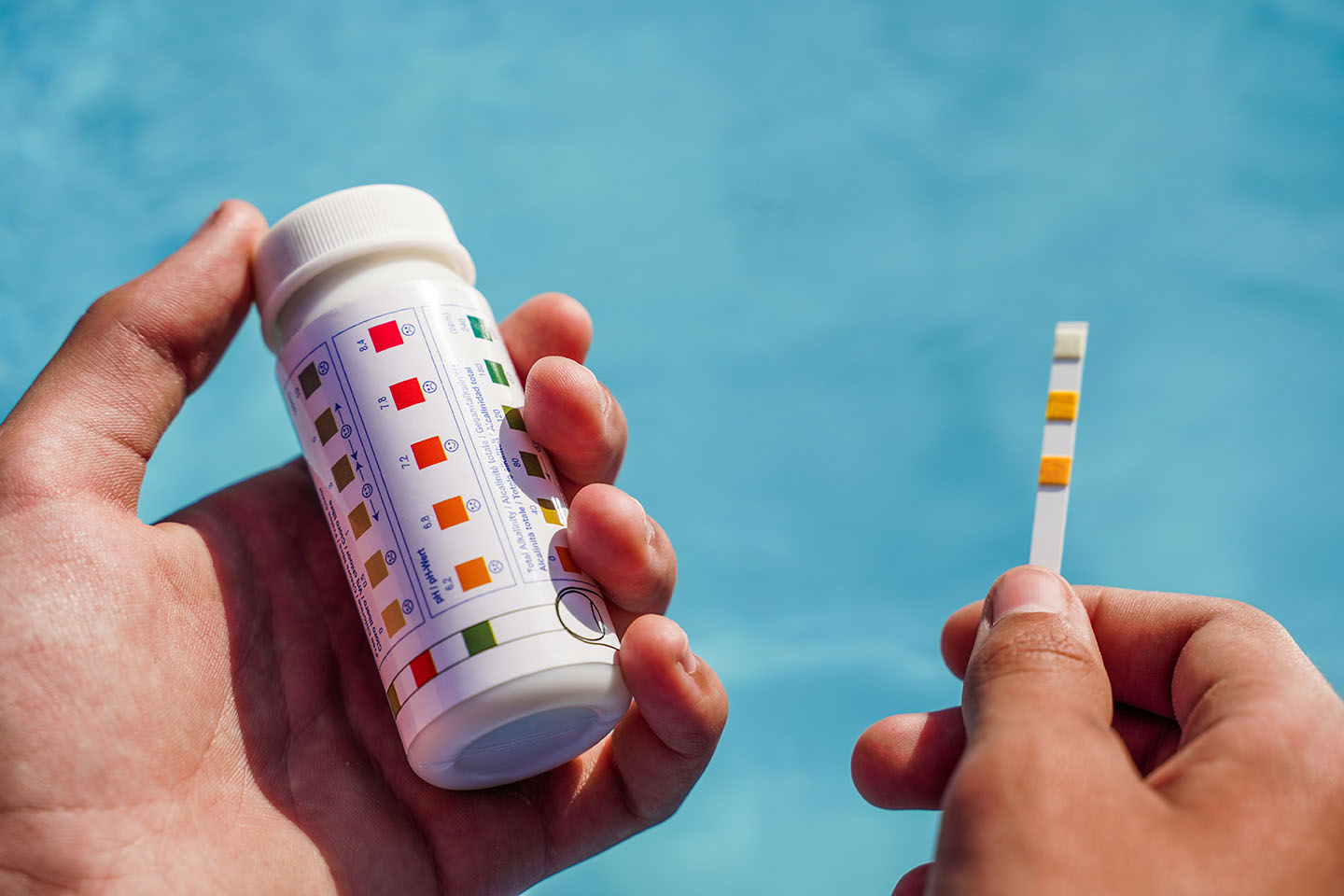
Chlorine is added to swimming pools in the form of chlorine tablets, granular chlorine, or liquid chlorine. The chlorine is then dissolved in the water and circulated throughout the pool. The amount of chlorine in a swimming pool needs to be regularly monitored and adjusted to maintain a safe level.
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17.
Noun:
Singular: chlorine.
Plural: chlorines.
Adjective:
Chlorine: relating to or containing the chemical element chlorine.
Verb:
Chlorinate: to treat with chlorine.
The word chlorine comes from the Greek word “khloros”, which means “greenish-yellow”. The word “khloros” is related to the word “chloros”, which means “yellowish-green”.
Why is chlorine added to swimming pools?
Question:
What is chlorine, and what are its primary uses in various scientific and industrial applications?
Answer:
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. It is a highly reactive, greenish-yellow gas at room temperature and is part of the halogen group on the periodic table.
Chlorine has numerous important uses in various scientific and industrial applications. It is commonly used in water treatment to disinfect and purify drinking water, making it safe for consumption by killing harmful bacteria and microorganisms. Additionally, chlorine is a key ingredient in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including plastics, solvents, and pesticides. It is also used in the manufacturing of paper, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
However, despite its essential applications, chlorine must be handled with care, as it can be toxic in high concentrations and poses health and environmental risks. Proper safety measures and handling protocols are crucial in its industrial and scientific use.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.