

Bones are organs that make up the skeleton. They are rigid and provide support for the body, protect organs, store minerals, and produce blood cells.
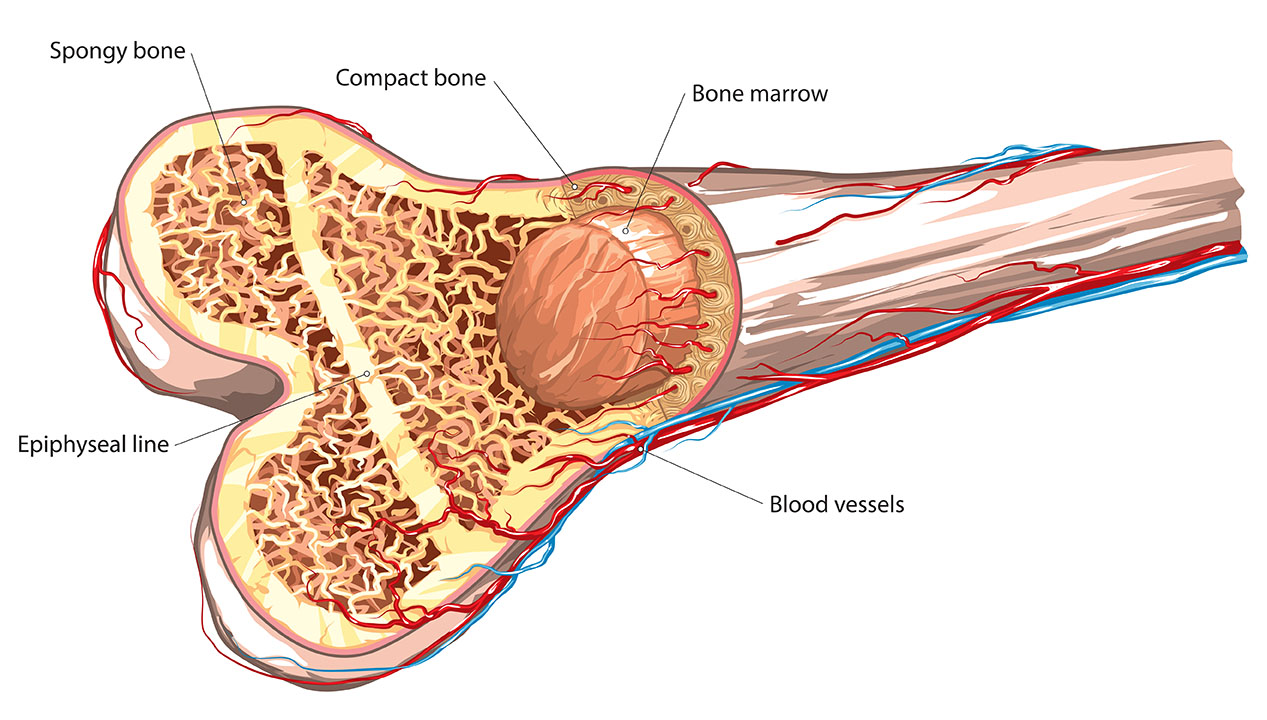
Bones are made up of two main types of tissue: compact bone and cancellous bone. Compact bone is the hard, outer layer of bone. It is made up of tightly packed bone cells. Cancellous bone is the spongy inner layer of bone. It is made up of a network of trabeculae, which are thin, bony plates.
Bones are also home to a number of other tissues, including bone marrow, blood vessels, and nerves. Bone marrow is the soft tissue that fills the cavities in bones. It is responsible for producing blood cells. Blood vessels bring nutrients and oxygen to bones, and nerves carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to bones.
Bones are constantly being remodelled, which means that they are being broken down and rebuilt. This process is important for keeping bones strong and healthy. The process of bone remodelling is regulated by a number of factors, including hormones, diet, and exercise.
Here are some of the functions of bones:
Here are some of the diseases that can affect bones:
The bones in my hand are aching.
Singular: bone.
Plural: bones.
Adjective: bony.
The word "bones" comes from the Old English word bān, which means "bone." The Old English word bān is thought to be related to the Proto-Germanic word bōnō, which also means "bone.".
How many bones make up the human skeleton?
Question:
What are the different types of bones in the human body?
Answer:
The human body has 206 bones, which are classified into four main types:
Long bones: Long bones are the longest bones in the body. They are used for support and movement. Examples of long bones include the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the humerus (upper arm bone).
Long bones.
Short bones: Short bones are the smallest bones in the body. They are used for support and stability. Examples of short bones include the carpals (wrist bones) and the tarsals (ankle bones).
Short bones.
Flat bones: Flat bones are thin and flat. They are used for protection and for providing a surface for muscle attachment. Examples of flat bones include the skull, the ribs, and the sternum (breastbone).
Flat bones.
Irregular bones: Irregular bones are any bones that do not fit into the other three categories. They are often used for protection or for providing a surface for muscle attachment. Examples of irregular bones include the vertebrae (bones in the spine) and the sacrum (bone at the base of the spine).
Irregular bones.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.