

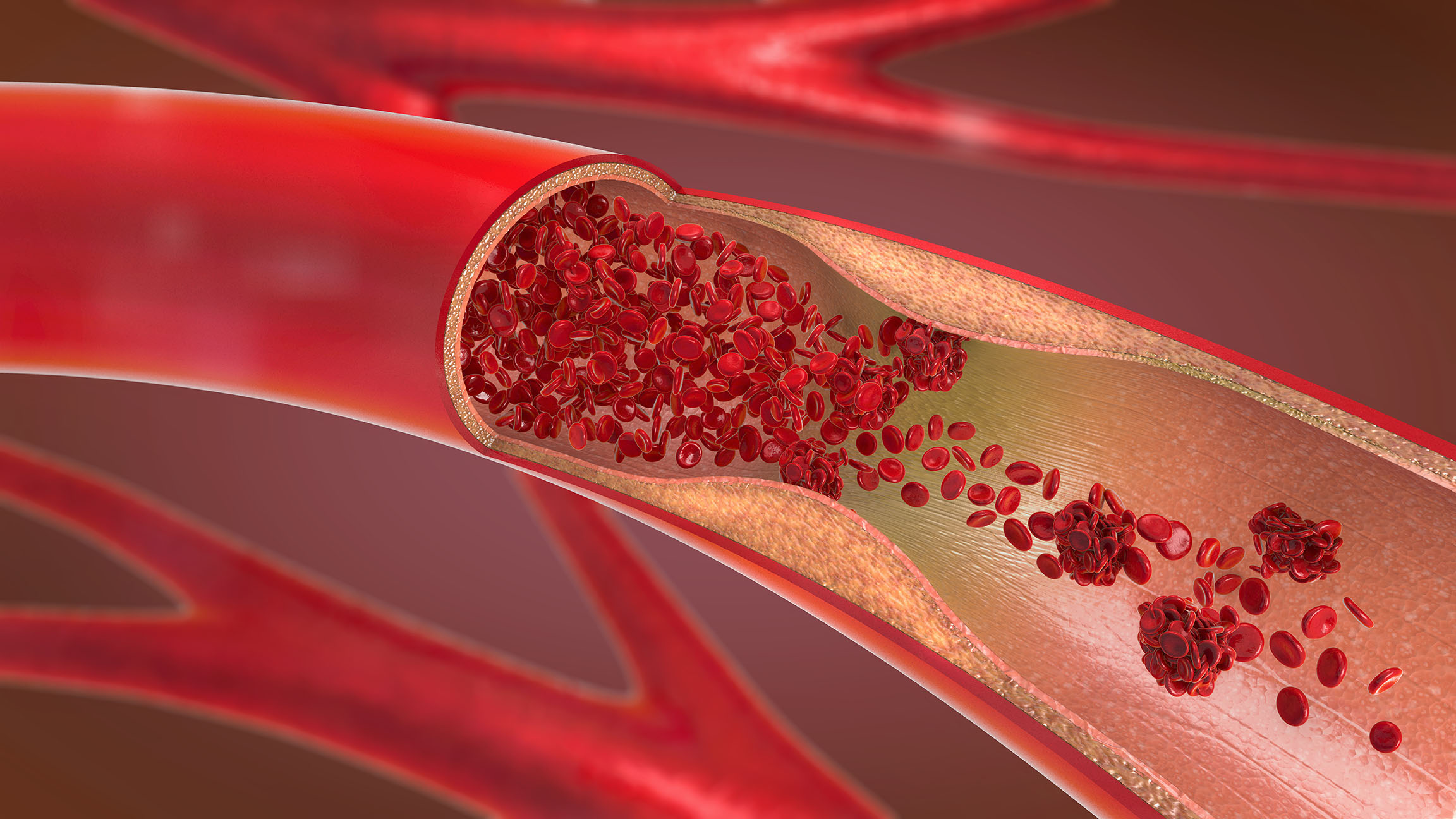
An artery is a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body. Arteries are typically large and have thick walls. They carry oxygen-rich blood to the body's tissues.
The walls of arteries are made up of three layers:
Arteries are named according to the organ or region of the body that they supply with blood. For example, the coronary arteries supply blood to the heart, and the carotid arteries supply blood to the head.
The doctor examined the patient's arterial blood pressure.
Noun: artery (plural: arteries).
Adjective: arterial.
Adverb: arterially.
Verb: arterialise (to make something arterial).
Gerund: arterialising.
Participle: arterialised.
The word artery comes from the Greek word ἀρτηρία (artēríā), which means "windpipe." This is because, in ancient times, it was believed that arteries carried air to the extremities of the body. The word ἀρτηρία is a compound word, consisting of the elements ἀήρ (aer), meaning "air," and τηρεῖν (terein), meaning "to keep.".
Where can arteries be found?
Question:
Define the term "artery" and explain its role in the circulatory system. Describe the main characteristics of arteries that enable them to perform their function effectively.
Answer: