

Amino acids are organic molecules that contain an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for life.
There are 20 different amino acids that are used to make proteins in the human body. Each amino acid has a different chemical structure, and this gives proteins their different properties.
The amino acids are linked together in a specific order to form proteins. The order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the protein.
Proteins are involved in many important functions in the body, including:
There are 20 different amino acids that are used to build proteins.
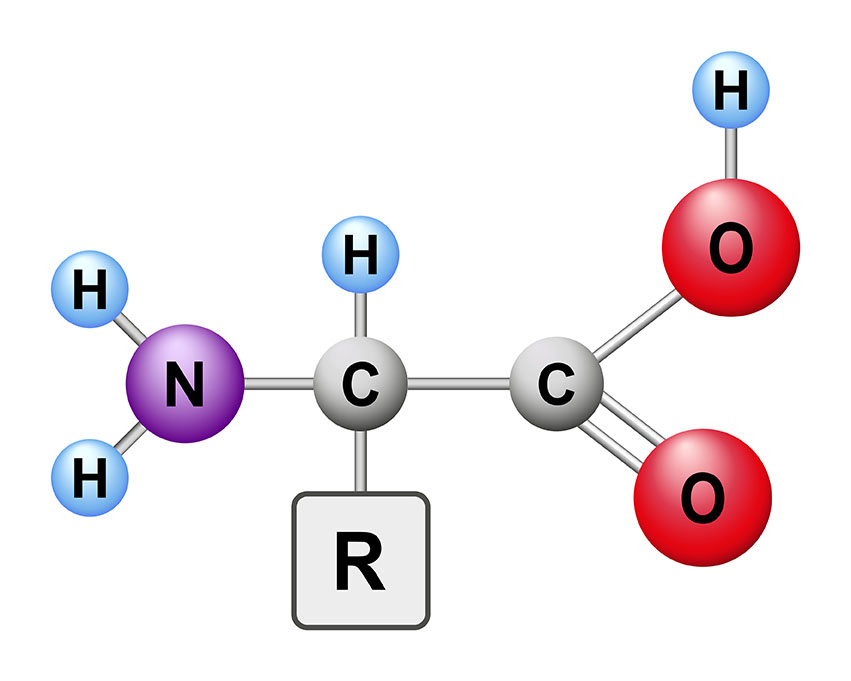
Noun: amino acid.
Adjective: amino acid.
Plural: amino acids.
Synonyms: protein building blocks, essential amino acids, non-essential amino acids.
Antonyms: none.
The word "amino acid" is derived from the Greek words amino (meaning "having an amine group") and acid (meaning "sour"). The first amino acid was discovered in 1806 by the French chemist Pierre Jean Robiquet. He named it "asparagine" after the asparagus plant, from which he isolated it.
How many amino acids are there?
Question:
Why are amino acids essential for life?
Answer:
There are 20 amino acids that are essential for life. These amino acids cannot be synthesised by the body and must be obtained from the diet.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.