

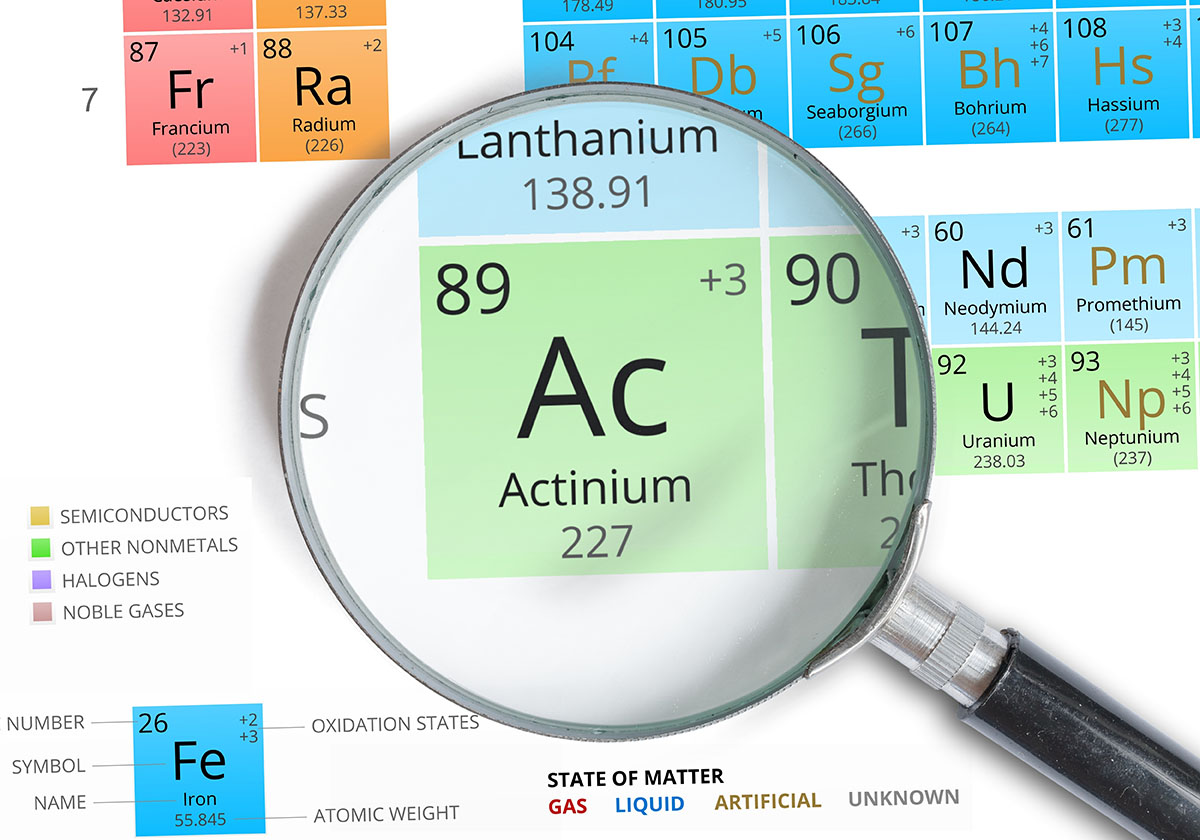
Actinium is a chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89. It is a radioactive element that is found in nature as a decay product of uranium. Actinium is a silvery-white metal that is soft and has a low melting point. It is also highly radioactive, and it emits alpha particles.
Actinium was discovered in 1899 by Pierre and Marie Curie. They were studying the radioactive decay of uranium when they discovered actinium. Actinium is named after the Greek word "aktis", which means "ray".
Actinium is not very common in nature, but it is found in some uranium ores. It is also produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Actinium is used in a variety of applications, including:
Actinium is a dangerous element, and it can be harmful to human health. It is important to handle actinium with care and to take precautions to avoid exposure.
Actinium can also be used to refer to a radioactive substance that is found in nature as a decay product of uranium.
Noun:
actinium (no plural form).
a chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89.
Adjective:
Verb:
The word actinium comes from the Greek word "aktis", which means "ray". It was named after this because actinium emits alpha particles, which are a type of radiation.
What is actinium?
Question:
Explain the position of actinium (Ac) in the Periodic Table and its key properties. Additionally, mention one significant application of actinium.
Answer:
Actinium (Ac) is an element placed in the actinide series, specifically below lanthanum (La) in the seventh row of the Periodic Table. It is a silvery-white, soft, and highly radioactive metal. The most stable isotope is Actinium-227, which emits alpha particles during radioactive decay. One significant application of actinium is its use as a neutron source in scientific research and certain industrial applications.
Address
Developing Experts Limited
Exchange Street Buildings
35-37 Exchange Street
Norwich
NR2 1DP
UK
Phone
01603 273515
Email
hello@developingexperts.com
Copyright 2025 Developing Experts, All rights reserved.